
Back انتخابات الرئاسة الأمريكية 1820 Arabic ھەڵبژاردنی سەرۆکایەتیی ویلایەتە یەکگرتووەکانی ئەمریکا (١٨٢٠) CKB Præsidentvalget i USA 1820 Danish Präsidentschaftswahl in den Vereinigten Staaten 1820 German Elecciones presidenciales de Estados Unidos de 1820 Spanish انتخابات ریاستجمهوری ایالات متحده آمریکا (۱۸۲۰) Persian Yhdysvaltain presidentinvaalit 1820 Finnish Élection présidentielle américaine de 1820 French הבחירות לנשיאות ארצות הברית 1820 HE Elezioni presidenziali negli Stati Uniti d'America del 1820 Italian
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
235 members[a] of the Electoral College 118 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 10.1%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
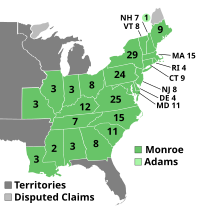 Presidential election results map. Green denotes states won by Monroe and light green denotes a New Hampshire elector William Plumer's vote for John Quincy Adams. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. Missouri's statehood status and subsequent electoral votes were disputed, and are therefore not counted in the above infobox. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in the United States from November 1 to December 6, 1820. Taking place at the height of the Era of Good Feelings, the election saw incumbent Democratic-Republican President James Monroe win reelection without a major opponent. It was the third and the most recent United States presidential election in which a presidential candidate ran effectively unopposed. James Monroe's re-election marked the first time in U.S. history that a third consecutive president won a second election.
Monroe and Vice President Daniel D. Tompkins faced little to no opposition from other Democratic-Republicans in their quest for a second term. The Federalist Party had fielded a presidential candidate in each election since 1796, but the party's already-waning popularity had declined further following the War of 1812. Although able to field a nominee for vice president, the Federalists could not put forward a presidential candidate, leaving Monroe without organized opposition.
Monroe won every state and received all but one of the electoral votes. Secretary of State John Quincy Adams received the only other electoral vote, which came from faithless elector William Plumer. Nine different Federalists received electoral votes for vice president, but Tompkins won re-election by a large margin. No other post-Twelfth Amendment presidential candidate has matched Monroe's electoral vote share. Monroe and George Washington remain the only presidential candidates to run without any major opposition. Monroe's victory was the last of six straight victories by Virginians in presidential elections (Jefferson twice, Madison twice, and Monroe twice). This was the last election in which an incumbent ticket was reelected until the ticket of Woodrow Wilson and Thomas R. Marshall were reelected in 1916.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
