
Back ২০১৭ উত্তর ভারত মহাসাগর ঘূর্ণিঝড় মৌসুম Bengali/Bangla Zyklonsaison im Nordindik 2017 German Temporada de ciclones en el Índico Norte de 2017 Spanish 2017년 북인도양 사이클론 Korean ฤดูพายุไซโคลนมหาสมุทรอินเดียเหนือ พ.ศ. 2560 Thai 2017年北印度洋氣旋季 Chinese
| 2017 North Indian Ocean cyclone season | |
|---|---|
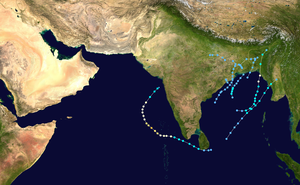 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | April 15, 2017 |
| Last system dissipated | December 9, 2017 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Ockhi |
| • Maximum winds | 155 km/h (100 mph) (3-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 976 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Depressions | 10 |
| Deep depressions | 6 |
| Cyclonic storms | 3 |
| Severe cyclonic storms | 2 |
| Very severe cyclonic storms | 1 |
| Super cyclonic storms | 0 |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | $3.65 billion (2017 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 2017 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below average yet deadly season in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. This season produced only three named storms, of which one only intensified into a very severe cyclonic storm. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December with the two peaks in May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. The season began with the formation Cyclone Maarutha on April 15 and ended with the dissipation of a deep depression on December 9.
The scope of this article is limited to the Indian Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere, east of the Horn of Africa and west of the Malay Peninsula. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean – the Arabian Sea to the west of the Indian subcontinent, abbreviated ARB by the India Meteorological Department (IMD); and the Bay of Bengal to the east, abbreviated BOB by the IMD. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the IMD, while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. On average, three to four cyclonic storms form in this basin every season.[1][2]
- ^ "Annual Frequency of Cyclonic Disturbances (Maximum Wind Speed of 17 Knots or More), Cyclones (34 Knots or More) and Severe Cyclones (48 Knots or More) Over the Bay of Bengal (BOB), Arabian Sea (AS) and Land Surface of India" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. Retrieved October 30, 2015.
- ^ RSMC – Tropical Cyclones New Delhi (2010). Report on Cyclonic Disturbances over North Indian Ocean during 2009 (PDF) (Report). India Meteorological Department. pp. 2–3. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 4, 2010. Retrieved May 24, 2011.