Back 61 Cygni Afrikaans 61 الدجاجة Arabic 61 Cygni AST 61 del Cigne Catalan 61 Cygni Czech 61 Cygni Danish 61 Cygni German 61 Cygni Spanish ۶۱ ماکیان Persian 61 Cygni Finnish
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| 61 Cygni A | |
| Right ascension | 21h 06m 53.9396s[1] |
| Declination | +38° 44′ 57.902″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.21[2] |
| 61 Cygni B | |
| Right ascension | 21h 06m 55.2638s[3] |
| Declination | +38° 44′ 31.359″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.05[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| 61 Cyg A | |
| Spectral type | K5V[2] |
| U−B color index | +1.155[5] |
| B−V color index | +1.139[5] |
| Variable type | BY Dra[6] |
| 61 Cyg B | |
| Spectral type | K7V |
| U−B color index | +1.242[5] |
| B−V color index | +1.320[5] |
| Variable type | Flare star[7] |
| Astrometry | |
| 61 Cygni A | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −65.97±0.12[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 4,164.209 mas/yr[1] Dec.: 3,249.614 mas/yr[1] |
| Parallax (π) | 285.9949 ± 0.0599 mas[1] |
| Distance | 11.404 ± 0.002 ly (3.4966 ± 0.0007 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 7.506[8] |
| 61 Cygni B | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −64.59±0.12[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 4,105.976 mas/yr[3] Dec.: 3,155.942 mas/yr[3] |
| Parallax (π) | 286.0054 ± 0.0289 mas[3] |
| Distance | 11.404 ± 0.001 ly (3.4964 ± 0.0004 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 8.228[8] |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Companion | 61 Cygni B |
| Period (P) | 678 ±34 yr |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 24.272 ±0.592″ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.49 ±0.03 |
| Inclination (i) | 51 ±2° |
| Longitude of the node (Ω) | 178 ±2° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 1709 ±16 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 149 ±6° |
| Details | |
| 61 Cygni A | |
| Mass | 0.70[10] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.665 ±0.005[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.153 ±0.01[11] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.40[12] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,526 ±66[13] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.20[12] dex |
| Rotation | 35.54±0.47 d[14] |
| Age | 6.1 ±1[11] Gyr |
| 61 Cygni B | |
| Mass | 0.63[10] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.595 ±0.008[11] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.085 ±0.007[11] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.20[12] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,077 ±59[13] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.27[12] dex |
| Rotation | 34.55±0.57 d[14] |
| Age | 6.1 ±1[11] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| 61 Cygni A: V1803 Cygni, HD 201091, HIP 104214, HR 8085, BD+38°4343, LHS 62, SAO 70919[6] | |
| 61 Cygni B: HD 201092, HIP 104217, HR 8086, BD+38°4344, LHS 63[7] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | The system |
| A | |
| B | |
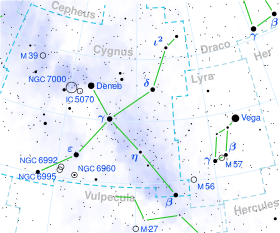
61 Cygni /ˈsɪɡni/ is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus, consisting of a pair of K-type dwarf stars that orbit each other in a period of about 659 years. Of apparent magnitude 5.20 and 6.05, respectively, they can be seen with binoculars in city skies or with the naked eye in rural areas without light pollution.
61 Cygni first attracted the attention of astronomers when its large proper motion was first demonstrated by Giuseppe Piazzi in 1804. In 1838, Friedrich Bessel measured its distance from Earth at about 10.4 light-years, very close to the actual value of about 11.4 light-years; this was the first distance estimate for any star other than the Sun, and first star to have its stellar parallax measured. Among all stars or stellar systems listed in the modern Hipparcos Catalogue, 61 Cygni has the seventh-highest proper motion, and the highest among all visible stars or systems.[note 1][16][17]
Over the course of the twentieth century, several different astronomers reported evidence of a massive planet orbiting one of the two stars, but recent high-precision radial velocity observations have shown that all such claims were unfounded.[18] No planets have been confirmed in this stellar system to date.
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
vallenari-2023awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
fischer-2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
vallenari-2023bwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
the internet stellar database-2011was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
catalano s-1979was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
simbadwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
simbad-2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
kovtyukh-2003was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
hartkopfwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
staff-2007bwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
kervella-2008was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
luck-2005was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
van belle-2009was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
olspert-2018was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "SIMBAD Query Result: ADS 14636 AB -- Double or multiple star". SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Archived from the original on 1 February 2014. Retrieved 3 February 2019. (61 Cygni)
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
staff-2007awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hipparcos: Catalogues: The Millennium Star Atlas: The Top 20 High Proper Motion Archived 28 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine, European Space Agency, retrieved 2019-06-27
- ^ Wittenmyer, R. A.; Endl, M.; Cochran, W.D.; Hatzes, A.; Walker, G. A. H.; Yang, S. L. S.; Paulson, D. B. (2006). "Detection limits from the McDonald Observatory planet search program". Astronomical Journal. 132 (1): 177–188. arXiv:astro-ph/0604171. Bibcode:2006AJ....132..177W. doi:10.1086/504942. S2CID 16755455.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).