
Back أدينازولام Arabic Adinazolam Catalan آدینازولام Persian Adinatsolaami Finnish Adinazolam French Adinazolam IG Adinazolam Italian Adinazolam Portuguese Adinazolam Romanian Adinazolam Serbo-Croatian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Deracyn |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Metabolites | N-desmethyladinazolam
N, N-didesmethyladinazolam estazolam alpha-hydroxy-alprazolam |
| Elimination half-life | < 3 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
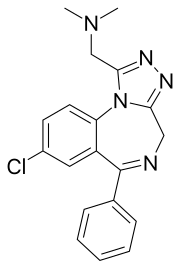
| Formula | C19H18ClN5 |
| Molar mass | 351.84 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 171–172.5 °C (339.8–342.5 °F) |
| Solubility in water | LogP: 4.16
Soluble in dichloromethane and methanol Salt (mesylate) soluble in water mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Adinazolam[1] (marketed under the brand name Deracyn) is a tranquilizer of the triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) class, which are benzodiazepines (BZDs) fused with a triazole ring. It possesses anxiolytic,[2] anticonvulsant, sedative, and antidepressant[3][4] properties. Adinazolam was developed by Jackson B. Hester, who was seeking to enhance the antidepressant properties of alprazolam, which he also developed.[5] Adinazolam was never FDA approved and never made available to the public market; however, it has been sold as a designer drug.[6]
- ^ FR 2248050, "4,5-dihydro-4h-s-triazolo (4,3-a) (1,4) benzodiazepine - cns depressants, anti-convulsants, anti-aggressives and somatic reflex in", issued 21 January 1977, assigned to Ciba-Geigy AG and Novartis AG.
- ^ Venkatakrishnan K, von Moltke LL, Duan SX, Fleishaker JC, Shader RI, Greenblatt DJ (March 1998). "Kinetic characterization and identification of the enzymes responsible for the hepatic biotransformation of adinazolam and N-desmethyladinazolam in man". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 50 (3): 265–274. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1998.tb06859.x. PMID 9600717. S2CID 33656240.
- ^ Dunner D, Myers J, Khan A, Avery D, Ishiki D, Pyke R (June 1987). "Adinazolam--a new antidepressant: findings of a placebo-controlled, double-blind study in outpatients with major depression". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 7 (3): 170–172. doi:10.1097/00004714-198706000-00010. PMID 3298327.
- ^ Lahti RA, Sethy VH, Barsuhn C, Hester JB (November 1983). "Pharmacological profile of the antidepressant adinazolam, a triazolobenzodiazepine". Neuropharmacology. 22 (11): 1277–1282. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(83)90200-9. PMID 6320036. S2CID 667962.
- ^ "Discovers Award 2004" (PDF). Special Publications. Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America. April 2004. p. 39. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 24, 2006. Retrieved August 18, 2006.
- ^ Moosmann B, Bisel P, Franz F, Huppertz LM, Auwärter V (November 2016). "Characterization and in vitro phase I microsomal metabolism of designer benzodiazepines - an update comprising adinazolam, cloniprazepam, fonazepam, 3-hydroxyphenazepam, metizolam and nitrazolam". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 51 (11): 1080–1089. Bibcode:2016JMSp...51.1080M. doi:10.1002/jms.3840. PMID 27535017.