
Back كحول أليلي Arabic Allylalkohol Czech Allylalkohol German 2-προπεν-1-όλη Greek Alila alkoholo Esperanto Alcohol alílico Spanish Alil alkohol Basque آلیل الکل Persian Allyylialkoholi Finnish Alcool allylique French
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Prop-2-en-1-ol | |
| Other names
Allyl alcohol
2-Propen-1-ol 1-Propen-3-ol[1] Vinyl carbinol[1] Allylic alcohol Weed drench[citation needed] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.156 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1098 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6O | |
| Molar mass | 58.080 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | mustard-like[1] |
| Density | 0.854 g/ml |
| Melting point | −129 °C |
| Boiling point | 97 °C (207 °F; 370 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Vapor pressure | 17 mmHg[1] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 15.5 (H2O)[2] |
| -36.70·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Highly toxic, lachrymator |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H301, H302, H311, H315, H319, H331, H335, H400 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P361, P362, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 21 °C (70 °F; 294 K) |
| 378 °C (712 °F; 651 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.5–18.0% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
80 mg/kg (rat, orally)[3] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
1000 ppm (mammal, 1 hr) 76 ppm (rat, 8 hr) 207 ppm (mouse, 2 hr) 1000 ppm (rabbit, 3.5 hr) 1000 ppm (monkey, 4 hr) 1060 ppm (rat, 1 hr) 165 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 76 ppm (rat, 8 hr)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
2 ppm[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2 ppm (5 mg/m3) ST 4 ppm (10 mg/m3) [skin] [1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
20 ppm[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
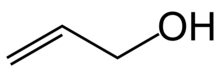
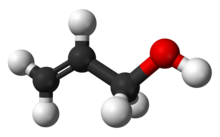
Allyl alcohol (IUPAC name: prop-2-en-1-ol) is an organic compound with the structural formula CH2=CHCH2OH. Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers.[5] Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols.
- ^ a b c d e f g h NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0017". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. p. 5–88. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ^ Allyl alcohol toxicity
- ^ "Allyl alcohol". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Ludger Krähling; Jürgen Krey; Gerald Jakobson; Johann Grolig; Leopold Miksche (2002). "Allyl Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_425. ISBN 978-3527306732.
