
Back أليل البنزين Arabic Alilbenzeno Esperanto Allilbenzene Italian Allylbenzeen Dutch Fenylopropen Polish Аллилбензол Russian 苯丙烯 Chinese
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Prop-2-enyl)benzene[1] | |
| Other names
3-Phenyl-1-propene; 2-Propenylbenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.542 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10 | |
| Molar mass | 118.179 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.893 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −40 °C (−40 °F; 233 K) |
| Boiling point | 156 °C (313 °F; 429 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flammable liquid and vapor, May be fatal if swallowed and enters airways |
| GHS labelling: | |
  [2] [2]
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H304[2] | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P280, P301+P316, P303+P361+P353, P331, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501[2] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
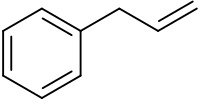
Allylbenzene or 3-phenylpropene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2CH=CH2. It is a colorless liquid. The compound consists of a phenyl group attached to an allyl group. Allylbenzene isomerizes to trans-propenylbenzene.[3]
In plant biochemistry, the allylbenzene skeleton is the parent (simplest representation) of many phenylpropanoids. Prominent allylbenzenes include eugenol, safrole, and many others.[4]
- ^ "Allylbenzene".
- ^ a b c "Allylbenzene".
- ^ Hassam, Mohammad; Taher, Abu; Arnott, Gareth E.; Green, Ivan R.; van Otterlo, Willem A. L. (2015). "Isomerization of Allylbenzenes". Chemical Reviews. 115 (11): 5462–5569. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00052. PMID 25993416.
- ^ Vogt, Thomas (2010). "Phenylpropanoid Biosynthesis". Molecular Plant. 3 (1): 2–20. doi:10.1093/mp/ssp106. PMID 20035037.