
Back نمر عربي Arabic نمر عربى ARZ Kraimol (Panthera pardus nimr) AVK Ərəbistan bəbiri Azerbaijani Арабски леопард Bulgarian Lleopard d'Aràbia Catalan Levhart arabský Czech Arabisk leopard Danish Αραβική λεοπάρδαλη Greek Panthera pardus nimr Spanish
| Arabian leopard | |
|---|---|

| |
| Leopard at Ein Gedi, Israel | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Felidae |
| Subfamily: | Pantherinae |
| Genus: | Panthera |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | P. p. nimr
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Panthera pardus nimr | |
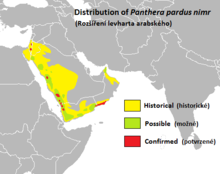
| |
| Distribution of the Arabian leopard | |
| Synonyms | |
|
P. p. jarvisl Pocock, 1932 | |
The Arabian leopard (Panthera pardus nimr) is the smallest leopard subspecies. It was described in 1830 and is native to the Arabian Peninsula, where it was widely distributed in rugged hilly and montane terrain until the late 1970s. Today, the population is severely fragmented and thought to decline continuously. In 2008, an estimated 45–200 individuals in three isolated subpopulations were restricted to western Saudi Arabia, Oman and Yemen. However, as of 2023, it is estimated that 100–120 in total remain, with 70-84 mature individuals, in Oman and Yemen, and it is possibly extinct in Saudi Arabia. The current population trend is suspected to be decreasing.[1]
- ^ a b Al Hikmani, H.; Spalton, A.; Zafar-ul Islam, M.; al-Johany, A.; Sulayem, M.; Al-Duais, M.; Almalki, A. (2024) [amended version of 2023 assessment]. "Panthera pardus ssp. nimr". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2024: e.T15958A259040222. Retrieved 20 July 2024.
