
Back Acetat de bari Catalan Bariumacetat German Οξικό βάριο Greek Baria acetato Esperanto Bariumasetaatti Finnish Acetato di bario Italian 酢酸バリウム Japanese ബേരിയം അസറ്റേറ്റ് Malayalam Bariumacetaat Dutch Octan baru Polish
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Barium acetate
| |
| Other names
Barium diacetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
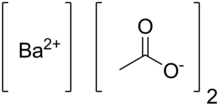
| Abbreviations | Ba(OAc)2 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.045 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6BaO4 | |
| Molar mass | 255.415 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.468 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.19 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 450 °C (842 °F; 723 K) decomposes |
| 55.8 g/100 mL (0 °C) 72 g/100mL (20 °C) | |
| Solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol, methanol |
| -100.1·10−6 cm3/mol (2H2O) | |
| Structure | |
| tetragonal | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic, hazardous on ingestion |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
108 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Barium acetate (Ba(C2H3O2)2) is the salt of barium(II) and acetic acid. Barium acetate is toxic to humans, but it has use in chemistry and manufacturing.

