Back Белоруссиа Abkhazian Bèlarusia ACE Белоруссие ADY Belarus Afrikaans Weißrussland ALS ቤላሩስ Amharic Belarus AMI Belarrusia AN Hwitrussland ANG Belarọs ANN
Republic of Belarus
| |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Дзяржаўны гімн Рэспублікі Беларусь (Belarusian) Dziaržaŭny Himn Respubliki Biełaruś Государственный гимн Республики Беларусь (Russian) Gosudarstvennyy gimn Respubliki Belarus "State Anthem of the Republic of Belarus" | |
| Capital and largest city | Minsk 53°55′N 27°33′E / 53.917°N 27.550°E |
| Official languages | |
| Recognized minority languages | |
| Ethnic groups (2021)[1] |
|
| Religion (2020)[2] |
|
| Demonym(s) | Belarusian |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic under a dictatorship[3][4][5] |
| Alexander Lukashenko[a] | |
| Roman Golovchenko[8] | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Council of the Republic | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
| 882 | |
| 25 March 1918 | |
| 1 January 1919 | |
| 31 July 1920 | |
| 27 July 1990 | |
| 25 August 1991 | |
| 19 September 1991 | |
| 15 March 1994 | |
| 8 December 1999 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 207,595 km2 (80,153 sq mi) (84th) |
• Water (%) | 1.4% (2.830 km2 or 1.093 sq mi)b |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 9,155,978[9] (98th) |
• Density | 45.8/km2 (118.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2019) | low inequality |
| HDI (2022) | very high (69th) |
| Currency | Belarusian ruble (BYN) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK[13]) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +375 |
| ISO 3166 code | BY |
| Internet TLD | |
| |
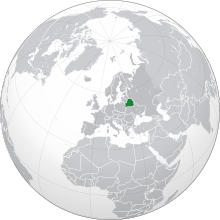
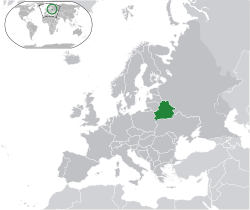
Belarus,[b] officially the Republic of Belarus,[c] is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) with a population of 9.1 million. The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into six regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status.
Between the medieval period and the 20th century, different states at various times controlled the lands of modern-day Belarus, including Kievan Rus', the Principality of Polotsk, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and the Russian Empire. In the aftermath of the Russian Revolution in 1917, different states arose competing for legitimacy amid the Civil War, ultimately ending in the rise of the Byelorussian SSR, which became a founding constituent republic of the Soviet Union in 1922. After the Polish-Soviet War (1918–1921), Belarus lost almost half of its territory to Poland. Much of the borders of Belarus took their modern shape in 1939, when some lands of the Second Polish Republic were reintegrated into it after the Soviet invasion of Poland, and were finalized after World War II. During World War II, military operations devastated Belarus, which lost about a quarter of its population and half of its economic resources. In 1945, the Byelorussian SSR became a founding member of the United Nations and the Soviet Union. The republic was home to a widespread and diverse anti-Nazi insurgent movement which dominated politics until well into the 1970s, overseeing Belarus' transformation from an agrarian to an industrial economy.
The parliament of the republic proclaimed the sovereignty of Belarus on 27 July 1990, and during the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Belarus gained independence on 25 August 1991. Following the adoption of a new constitution in 1994, Alexander Lukashenko was elected Belarus's first president in the country's first and only free election after independence, serving as president ever since. Lukashenko heads a highly centralized authoritarian government. Belarus ranks low in international measurements of freedom of the press and civil liberties. It has continued several Soviet-era policies, such as state ownership of large sections of the economy. Belarus is the only European country that continues to use capital punishment. In 2000, Belarus and Russia signed a treaty for greater cooperation, forming the Union State.
The country has been a member of the United Nations since its founding and has joined the CIS, the CSTO, the EAEU, the OSCE, and the Non-Aligned Movement. It has shown no aspirations of joining the European Union but maintains a bilateral relationship with the bloc, and also participates in the Baku Initiative.
- ^ "Belarus in figures 2021" (PDF). National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2021.
- ^ "Generations and Gender Survey, 2020 Belarus Wave 1". ggpsurvey.ined.fr. Archived from the original on 16 October 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2019.
- ^ "Belarus". CIA World Factbook. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ^ John R. Short (25 August 2021). Geopolitics: Making Sense of a Changing World. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 163 ff. ISBN 978-1-5381-3540-2. OCLC 1249714156.
- ^ Constitution of Belarus, 106, 97.5 97.7.
- ^ "Belarus leader Lukashenko holds secret inauguration amid continuing protests". france24.com. 23 September 2020.
- ^ "Belarus: Mass protests after Lukashenko secretly sworn in". BBC News. 23 September 2020.
Several EU countries and the US say they do not recognise Mr. Lukashenko as the legitimate president of Belarus.
- ^ "Lukashenko appoints new government". eng.belta.by. 19 August 2020.
- ^ "Population at the beginning of 2024" (PDF). belstat.gov.by.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (Belarus)". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. 10 October 2023. Retrieved 13 October 2023.
- ^ "GINI index (World Bank estimate) – Belarus". World Bank. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "Time Zone & Clock Changes in Minsk, Belarus". timeanddate.com.
- ^ "Icann Адобрыла Заяўку Беларусі На Дэлегаванне Дамена Першага Ўзроўню З Падтрымкай Алфавітаў Нацыянальных Моў.Бел". Retrieved 26 August 2014.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).