
Back متلازمة العروة العمياء Arabic Kor həlqə sindromu Azerbaijani Síndrome de la nansa cega Catalan Syndrom der blinden Schlinge German Syndrome de l'anse borgne French Синдром слепой кишечной петли Russian
| Blind loop syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Stagnant loop syndrome |
 | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
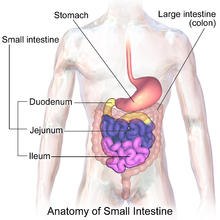
Blind loop syndrome, also known as stagnant loop syndrome,[1] is a state that occurs when the normal bacterial flora of the small intestine proliferates to numbers that cause significant derangement to the normal physiological processes of digestion and absorption. In some cases of blind loop syndrome, overgrowth of pathogenic non-commensal bacteria has also been noted. It has long been understood that from birth, and throughout life, large amounts of bacteria reside symbiotically within animal gastrointestinal tracts such as the human gastrointestinal tract. The understanding of this gut flora has even led to novel treatments for bowel irregularity that utilize so called "probiotics" or good bacteria that aid in normal digestion. The problem of blind loop syndrome arises when the bacterial colonies residing in the upper gastrointestinal tract begin to grow out of control or are altered in their makeup thereby creating a burden on the normal physiological processes occurring in the small intestine. This results in problems, among others, of: vitamin B12 deficiency, fat malabsorption and steatorrhea, fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies and intestinal wall injury.
- ^ Swan, Robert W. (December 1974). "Stagnant loop syndrome resulting from small-bowel irradiation injury and intestinal by-pass". Gynecologic Oncology. 2 (4): 441–445. doi:10.1016/0090-8258(74)90052-3. PMID 4618545.