
Back جسم القضيب Arabic Tijelo penisa BS Corpo del pene Italian Тело на пенис Macedonian Corpo do pênis Portuguese Corpul penisului Romanian ตัวองคชาต Thai
| Body of the penis | |
|---|---|
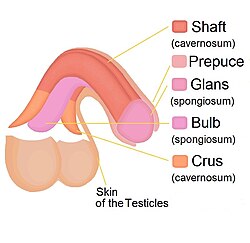 Diagram of penis. Body (labeled as shaft) at the top. | |
 The constituent cavernous cylinders of the penis. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Genital tubercle |
| Part of | Penis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | corpus penis |
| TA98 | A09.4.01.003 |
| TA2 | 3664 |
| FMA | 18249 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The body or shaft of the penis is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity.[1] It is the continuation of the internal root, which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans.[2] It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum, which becomes a complete one before the penile crura.[3] The body of the penis is homologous to the female clitoral body.[4][5][6]
- ^ "Penis anatomy: Functions and common conditions". www.medicalnewstoday.com. 2021-06-14. Retrieved 2023-03-13.
- ^ "The Penis - Structure - Muscles - Innervation - TeachMeAnatomy". teachmeanatomy.info. Retrieved 2023-03-13.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hsu2018was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Rodgers, Joann (2003). Sex: A Natural History. Henry Holt and Company. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-80507-281-5. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Gormley-Fleming, Elizabeth; Peate, Ian (2021). Fundamentals of Children and Young People's Anatomy and Physiology: A Textbook for Nursing and Healthcare Students. Wiley. p. 307. ISBN 978-1-11961-924-6. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Greenberg, Jerrold S.; Bruess, Clint E.; Oswalt, Sara B. (2014). Exploring the Dimensions of Human Sexuality. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 259. ISBN 978-1-44964-851-0. Retrieved September 29, 2023.