
Back بوتيل هيدروكسي تولوين Arabic İonol Azerbaijani دیبوتیل هیدروکسی تولوئن AZB Butil-hidroxitoluè Catalan Butylhydroxytoluen Czech Butylhydroxytoluol German Butilhidroxitolueno Spanish دیبوتیل هیدروکسی تولوئن Persian Butyloitu hydroksitolueeni Finnish Hydroxytoluène butylé French
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
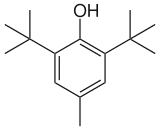
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.439 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E321 (antioxidants, ...) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24O | |
| Molar mass | 220.356 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to yellow powder |
| Odor | Slight, phenolic |
| Density | 1.048 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 70 °C (158 °F; 343 K)[4] |
| Boiling point | 265 °C (509 °F; 538 K)[4] |
| 1.1 mg/L (20 °C)[1] | |
| log P | 5.32[2] |
| Vapor pressure | 0.01 mmHg (20 °C)[3] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Flammable |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H410 | |
| P273, P391, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 127 °C (261 °F; 400 K)[4] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
> 2,000 mg/kg (dermal, rat)[6] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
None[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 mg/m3[3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[3] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [5] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Butylated hydroxyanisole |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), also known as dibutylhydroxytoluene, is a lipophilic organic compound, chemically a derivative of phenol, that is useful for its antioxidant properties.[7] BHT is widely used to prevent free radical-mediated oxidation in fluids (e.g. fuels, oils) and other materials, and the regulations overseen by the U.S. F.D.A.—which considers BHT to be "generally recognized as safe"—allow small amounts to be added to foods. Despite this, and the earlier determination by the National Cancer Institute that BHT was noncarcinogenic in an animal model, societal concerns over its broad use have been expressed. BHT has also been postulated as an antiviral drug, but as of December 2022, use of BHT as a drug is not supported by the scientific literature and it has not been approved by any drug regulatory agency for use as an antiviral.[citation needed]
- ^ KEMI Anställd [KEMI Staff] (1994). "Teknisk beskrivning av ämnet—2,6-Bis(tert-butyl)-4-metylfenol 1994 [Information on substances—2,6-Bis(tert-butyl)-4-methylphenol 1994]" (in Swedish and English). Sundyberg, SE: KEMI [Swedish Chemicals Agency]. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
Vattenlöslighet: 1,1 mg/L (20 °C) [Water solubility: 1.1 mg/L (20 °C)]
[better source needed] - ^ "2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol". www.chemsrc.com.
- ^ a b c d NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0246". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c "ICSC 0841 - BUTYLATED HYDROXYTOLUENE". www.inchem.org. March 1999.
- ^ "Safety data for 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol". ptcl.chem.ox.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 21 June 2002. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
- ^ Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ^ Yehye WA, Rahman NA, Ariffin A, Abd Hamid SB, Alhadi AA, Kadir FA, Yaeghoobi M (28 August 2015). "Understanding the Chemistry Behind the Antioxidant Activities of Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT): A Review". Eur. J. Med. Chem. 101: 295–312. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.06.026. PMID 26150290.
