
Back کانابینول AZB Cannabinol Catalan Kanabinol Czech Cannabinol Danish Cannabinol German Cannabinol Spanish Kannabinoli Finnish Cannabinol French Cannabinól Irish Kannabinol Hungarian
 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.216.772 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
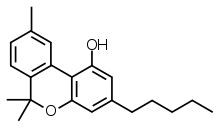
| Formula | C21H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 310.437 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 76–77 °C (169–171 °F) [1] |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble in water,[2] soluble in methanol[3] and ethanol[4] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid (e.g., cannabidiol (CBD)) that acts as a low affinity partial agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This activity at CB1 and CB2 receptors constitutes interaction of CBN with the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Although CBN shares the same mechanism of action as other phytocannabinoids (e.g., Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ9-THC), it has a lower affinity for CB1 receptors, meaning that much higher doses of CBN are required in order to experience effects, such as mild sedation.
It was the first cannabinoid to be isolated from cannabis and was discovered in 1896.
- ^ Cannabinol from PubChem
- ^ Lide DR (2012). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press. pp. 3–90. ISBN 978-1-43988049-4.
- ^ "Cannabinol solution, analytical standard, for drug analysis". Sigma-Aldrich. c046.
- ^ "Cannabinol" (PDF). Biotrend. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 22, 2016.