 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
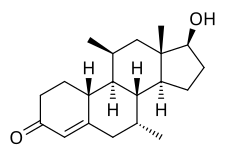
| Other names | CDB-1321; Dimethylnandrolone; 7α,11β-Dimethyl-19-nortestosterone; 7α,11β-Dimethylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one; 7α,11β-Dimethyl-19-norandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Progestogen |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 302.458 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dimethandrolone (DMA), also known by its developmental code name CDB-1321, is an experimental androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) and progestogen medication which is under investigation for potential clinical use.[1][2][3]
Dimethandrolone is an AAS, and hence is an agonist of the androgen receptor, the biological target of androgens like testosterone.[1] It is also a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone.[1] Due to its androgenic and progestogenic activity, dimethandrolone has antigonadotropic effects.[1] It has no estrogenic activity.[1][4]
Dimethandrolone was first described in 1997.[5] It was developed by the Contraceptive Development Branch of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, an agency in the United States government.[1][6]
An ester and prodrug of dimethandrolone, dimethandrolone undecanoate (DMAU) (CDB-4521), is under development for potential use as a birth control pill for men and in androgen replacement therapy for men.[1][2][3][7]
- ^ a b c d e f g Attardi BJ, Hild SA, Reel JR (June 2006). "Dimethandrolone undecanoate: a new potent orally active androgen with progestational activity". Endocrinology. 147 (6): 3016–26. doi:10.1210/en.2005-1524. PMID 16497801. S2CID 45745191.
- ^ a b Attardi BJ, Hild SA, Koduri S, Pham T, Pessaint L, Engbring J, et al. (October 2010). "The potent synthetic androgens, dimethandrolone (7α,11β-dimethyl-19-nortestosterone) and 11β-methyl-19-nortestosterone, do not require 5α-reduction to exert their maximal androgenic effects". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 122 (4): 212–8. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.06.009. PMC 2949447. PMID 20599615.
- ^ a b Wang C, Swerdloff RS (November 2010). "Hormonal approaches to male contraception". Current Opinion in Urology. 20 (6): 520–4. doi:10.1097/MOU.0b013e32833f1b4a. PMC 3078035. PMID 20808223.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid18555683was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
US5952319Awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid21164142was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Dimethandrolone undecanoate shows promise as a male birth control pill". Press Release. Endocrine Society. March 18, 2018.
