
Back تخطيط الصدى الدوبلري Arabic Ecografia Doppler Catalan Farbkodierte Doppler-Sonografie German Ecografía Doppler Spanish سونوگرافی فراصوتی داپلر Persian Échographie Doppler French Ecografía Doppler Galician בדיקת אולטרסאונד דופלר HE Ecografia Doppler Italian Ultrasonografia dopplerowska Polish
| Doppler ultrasonography, duplex ultrasonography | |
|---|---|
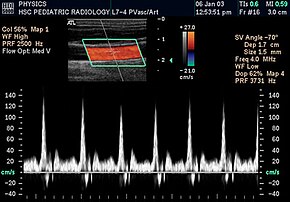 Spectral duplex scan of the common carotid artery | |
| MeSH | D018616 |
| MedlinePlus | 003433 |

Doppler ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography that employs the Doppler effect to perform imaging of the movement of tissues and body fluids (usually blood),[1][2] and their relative velocity to the probe. By calculating the frequency shift of a particular sample volume, for example, flow in an artery or a jet of blood flow over a heart valve, its speed and direction can be determined and visualized.
Duplex ultrasonography sometimes refers to Doppler ultrasonography or spectral Doppler ultrasonography.[3] Doppler ultrasonography consists of two components: brightness mode (B-mode) showing anatomy of the organs, and Doppler mode (showing blood flow) superimposed on the B-mode. Meanwhile, spectral Doppler ultrasonography consists of three components: B-mode, Doppler mode, and spectral waveform displayed at the lower half of the image. Therefore, "duplex ultrasonography" is a misnomer for spectral Doppler ultrasonography, and more exact name should be "triplex ultrasonography".[3]
This is particularly useful in cardiovascular studies (sonography of the vascular system and heart) and essential in many areas such as determining reverse blood flow in the liver vasculature in portal hypertension.
- ^ Srivastav, A.; Bhogi, K.; Mandal, S.; Sharad, M. (Aug 2019). "An Adaptive Low-Complexity Abnormality Detection Scheme for Wearable Ultrasonography". IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems. 66 (8): 1466–1470. doi:10.1109/TCSII.2018.2881612. S2CID 117391787.
- ^ Franceschi C (1978). L'Investigation vasculaire par ultrasonographie doppler. Masson. ISBN 2-225-63679-6.
- ^ a b McNaughton, Dean Alexander; Abu-Yousef, Monzer M. (January 2011). "Doppler US of the Liver Made Simple". RadioGraphics. 31 (1): 161–188. doi:10.1148/rg.311105093. ISSN 0271-5333. PMID 21257940.