
Back Fibromialgie Afrikaans ألم عضلي ليفي Arabic Fibromialxa AST Fibromialgiya Azerbaijani فیبرومیالژی AZB Фибромиалгия Bulgarian ফাইব্রোমায়ালজিয়া Bengali/Bangla Fibromiàlgia Catalan فایبرۆمایێلجا CKB Fibromyalgie Czech
| Fibromyalgia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Fibromyalgia syndrome |
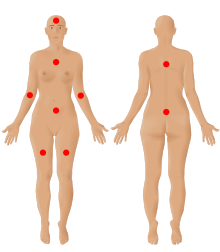 | |
| The nine possible pain sites of fibromyalgia according to the American Pain Society. | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology, neurology[2] |
| Symptoms | Widespread pain, feeling tired, sleep problems[3][4] |
| Usual onset | Early-Middle age[5] |
| Duration | Long term[3] |
| Causes | Unknown[4][5] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms after ruling out other potential causes[4][5] |
| Differential diagnosis | Anemia, autoimmune disorders (such as ankylosing spondylitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, or multiple sclerosis), Lyme disease, osteoarthritis, thyroid disease[6][7] |
| Treatment | Sufficient sleep and exercise[5] |
| Medication | Duloxetine, milnacipran, pregabalin, gabapentin[5][8] |
| Prognosis | Normal life expectancy[5] |
| Frequency | 2%[4] |
Fibromyalgia is a medical syndrome that causes chronic widespread pain, accompanied by fatigue, awakening unrefreshed, and cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include headaches, lower abdominal pain or cramps, and depression.[9] People with fibromyalgia can also experience insomnia[10] and general hypersensitivity.[11][12] The cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, but is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.[4] Environmental factors may include psychological stress, trauma, and some infections.[4] Since the pain appears to result from processes in the central nervous system, the condition is referred to as a "central sensitization syndrome".[4][13] Although a protocol using an algometer (algesiometer) for determining central sensitization has been proposed as an objective diagnostic test, fibromyalgia continues to be primarily diagnosed by exclusion.[14]
Fibromyalgia was first defined in 1990, with updated criteria in 2011,[4] 2016,[9] 2019.[12] The term 'fibromyalgia' is from Neo-Latin fibro-, meaning 'fibrous tissues', Greek μυο- myo-, 'muscle', and Greek άλγος algos, 'pain'; thus, the term literally means "'muscle and fibrous connective tissue pain'.[15] Fibromyalgia is estimated to affect 2 to 4% of the population.[16] Women are affected about twice as often as men.[4][16] Rates appear similar across areas of the world and among varied cultures.[4]
The treatment of fibromyalgia is symptomatic[17] and multidisciplinary.[18] The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology strongly recommends aerobic and strengthening exercise.[18] Weak recommendations are given to mindfulness, psychotherapy, acupuncture, hydrotherapy, and meditative exercise such as qigong, yoga, and tai chi.[18] The use of medication in the treatment of fibromyalgia is debated,[18][19] although antidepressants can improve quality of life.[20] Common helpful medications include other serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants.[21] Q10 coenzyme and vitamin D supplements may reduce pain and improve quality of life.[22] While fibromyalgia is persistent in nearly all patients, it does not result in death or tissue damage.[19]
- ^ "fibromyalgia". Collins Dictionaries. Archived from the original on 4 October 2015. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ "Neurology Now: Fibromyalgia: Is Fibromyalgia Real? | American Academy of Neurology". tools.aan.com. October 2009. Retrieved 1 June 2018.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
pmid21303476was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j Clauw DJ (April 2014). "Fibromyalgia: a clinical review". JAMA. 311 (15): 1547–1555. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3266. PMID 24737367. S2CID 43693607.
- ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
NIH2014Txwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Ferri FF (2010). "Chapter F". Ferri's differential diagnosis: a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby. ISBN 978-0-323-07699-9.
- ^ Schneider MJ, Brady DM, Perle SM (2006). "Commentary: differential diagnosis of fibromyalgia syndrome: proposal of a model and algorithm for patients presenting with the primary symptom of chronic widespread pain". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 29 (6): 493–501. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2006.06.010. PMID 16904498.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Coch2017Gabwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Häuser W, Katz RL, et al. (December 2016). "2016 Revisions to the 2010/2011 fibromyalgia diagnostic criteria". Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 46 (3): 319–329. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.08.012. PMID 27916278.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Wu-2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hauser2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Arnold-2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Central sensitivity and fibromyalgiwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:6was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Bergmann U (2012). Neurobiological foundations for EMDR practice. New York: Springer Pub. Co. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-8261-0938-5.
- ^ a b Fitzcharles MA, Cohen SP, Clauw DJ, Littlejohn G, Usui C, Häuser W (May 2021). "Nociplastic pain: towards an understanding of prevalent pain conditions". Lancet. 397 (10289): 2098–2110. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00392-5. PMID 34062144. S2CID 235245552.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Prab2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
Macfarlane-2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Hauser2018was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Mascarenhas-2021was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Kia S, Choy E (May 2017). "Update on Treatment Guideline in Fibromyalgia Syndrome with Focus on Pharmacology". Biomedicines. 5 (2): 20. doi:10.3390/biomedicines5020020. PMC 5489806. PMID 28536363.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Ibáñez-Vera-2018was invoked but never defined (see the help page).