
Back غليسرألديهيد Arabic قلیسرآلدئید AZB Глицералдехид Bulgarian গ্লিসারাল্ডিহাইড Bengali/Bangla Gliceraldehid BS Gliceraldehid Catalan Glyceraldehyd Czech Glycerinaldehyd German Γλυκεριναλδεΰδη Greek Gliceraldehído Spanish
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
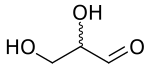
Glyceraldehyde
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydroxypropanal | |
| Other names
Glyceraldehyde
Glyceric aldehyde Glyceral | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.264 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C3H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 90.078 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.455 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) |
| Boiling point | 140 to 150 °C (284 to 302 °F; 413 to 423 K) at 0.8 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Glyceraldehyde (glyceral) is a triose monosaccharide with chemical formula C3H6O3. It is the simplest of all common aldoses. It is a sweet, colorless, crystalline solid that is an intermediate compound in carbohydrate metabolism. The word comes from combining glycerol and aldehyde, as glyceraldehyde is glycerol with one alcohol group oxidized to an aldehyde.
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4376