
Back Kammerwinkel German Gonioskopija Croatian Gonioscopia Italian Gonioskopia Polish Гониоскопия Russian Gonioskopija Serbo-Croatian Гониоскопија Serbian Гониоскопия Tatar
| Gonioscopy | |
|---|---|
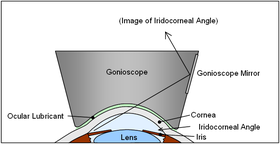 Goldmann Goniolens schematic | |
| Specialty | optometry, ophthalmology |
| MeSH | D006068 |
In ophthalmology, gonioscopy is a routine procedure that measures the angle between the iris and the cornea (the iridocorneal angle), using a goniolens (also known as a gonioscope) together with a slit lamp or operating microscope.[1][2] Its use is important in diagnosing and monitoring various eye conditions associated with glaucoma.
- ^ Cutolo CA, Bonzano C, Scotto R, Iester M, Bagnis A, Pizzorno C, et al. (December 2021). "Moving beyond the Slit-Lamp Gonioscopy: Challenges and Future Opportunities". Diagnostics. 11 (12): 2279. doi:10.3390/diagnostics11122279. PMC 8700682. PMID 34943516.
- ^ Alward WL (January 2011). "A history of gonioscopy". Optometry and Vision Science. 88 (1): 29–35. doi:10.1097/OPX.0b013e3181fc3718. PMID 20966801. S2CID 205908099.