| Gray graph | |
|---|---|
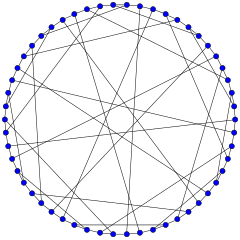 The Gray graph | |
| Named after | Marion Cameron Gray |
| Vertices | 54 |
| Edges | 81 |
| Radius | 6 |
| Diameter | 6 |
| Girth | 8 |
| Automorphisms | 1296 |
| Chromatic number | 2 |
| Chromatic index | 3 |
| Genus | 7 |
| Book thickness | 3 |
| Queue number | 2 |
| Properties | Cubic Semi-symmetric Hamiltonian Bipartite |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Gray graph is an undirected bipartite graph with 54 vertices and 81 edges. It is a cubic graph: every vertex touches exactly three edges. It was discovered by Marion C. Gray in 1932 (unpublished), then discovered independently by Bouwer 1968 in reply to a question posed by Jon Folkman 1967. The Gray graph is interesting as the first known example of a cubic graph having the algebraic property of being edge but not vertex transitive (see below).
The Gray graph has chromatic number 2, chromatic index 3, radius 6 and diameter 6. It is also a 3-vertex-connected and 3-edge-connected non-planar graph.
