
Back صمغة Arabic Гума (паталогія) Byelorussian Goma (patologia) Catalan Gumma Czech Goma granulomatosa Spanish گوم (آسیبشناسی) Persian גומא (פתולוגיה) HE Гумма Kazakh 고무종 Korean Гумма (медицина) Russian
| Gumma (pathology) | |
|---|---|
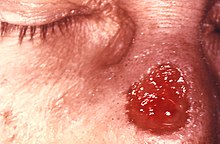 | |
| Gumma of nose due to a long-standing tertiary syphilitic infection. | |
| Specialty | Infectious diseases |

A gumma (plural gummata or gummas) is a soft, non-cancerous growth resulting from the tertiary stage of syphilis (and yaws[1]).
It is a form of granuloma.[2] Gummas are most commonly found in the liver (gumma hepatis), but can also be found in brain, heart, skin, bone, testis, and other tissues, leading to a variety of potential problems including neurological disorders or heart valve disease.
- ^ Marks M (August 2018). "Advances in the Treatment of Yaws". Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 3 (3): 92. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3030092. PMC 6161241. PMID 30274488.
- ^ Ghanem, Khalil G.; Hook, Edward W. (2020). "303. Syphilis". In Goldman, Lee; Schafer, Andrew I. (eds.). Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Vol. 2 (26th ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier. p. 1985. ISBN 978-0-323-55087-1.