
Back أسيتات الليثيوم Arabic لیتیوم استات AZB Lithiumacetat German Litia acetato Esperanto Acetato de litio Spanish لیتیم استات Persian Litiumasetaatti Finnish Acétate de lithium French लिथियम एसीटेट Hindi Acetato di litio Italian
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.105 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | C488804 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3LiO2 | |
| Molar mass | 65.98 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | crystal |
| Density | 1.26 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 286 °C (547 °F; 559 K) |
| 45.0 g/100 mL[1] | |
| −34.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
toxic |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
500 mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
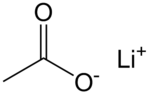
Lithium acetate (CH3COOLi) is a salt of lithium and acetic acid. It is often abbreviated as LiOAc.
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 465. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
