
Back العضلات الخراطينية لليد Arabic Músculs lumbricals de la mà Catalan Musculi lumbricales (Hand) German Músculos lumbricales de la mano Spanish ماهیچههای کرمی دست Persian Muscle lombrical de la main French Músculos lumbricais da man Galician השרירים התולעיים (כף יד) HE Musculi lumbricales manus Hungarian Muscoli lombricali della mano Italian
| Lumbricals of the hand | |
|---|---|
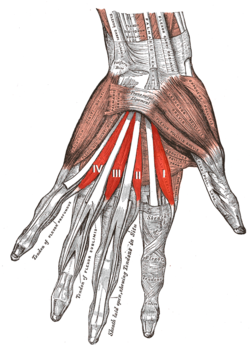 The muscles of the left hand. Palmar surface. (first lumbricalis labeled at bottom right of muscular group) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Flexor digitorum profundus |
| Insertion | Extensor expansion |
| Artery | Superficial palmar arch, common palmar digital arteries, deep palmar arch, dorsal digital artery |
| Nerve | Third and fourth deep branch of ulnar nerve, first and second median nerve |
| Actions | Flex metacarpophalangeal joints, extend interphalangeal joints |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculi lumbricales manus |
| TA98 | A04.6.02.065 |
| TA2 | 2532 |
| FMA | 37385 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The lumbricals are intrinsic muscles of the hand that flex the metacarpophalangeal joints,[1] and extend the interphalangeal joints.[1][2]
The lumbrical muscles of the foot also have a similar action, though they are of less clinical concern.
- ^ a b Gosling JA, Harris PF, Humpherson JR, Whitmore I, Willan PL (2008). Human Anatomy: Color Atlas and Textbook (5th ed.). Philadelphia: Mosby. ISBN 978-0-7234-3451-1. p. 97
- ^ Bilge O, Pinar Y, Ozer MA, Govsa F (October 2007). "The vascular anatomy of the lumbrical muscles in the hand". Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery. 60 (10): 1120–6. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2006.06.023. PMID 17825776.