Back Melville-eiland Afrikaans جزيرة ميلفيل (الأقاليم الشمالية الغربية ونونافوت) Arabic Islla Melville AST Melvill (ada) Azerbaijani Мелвилл (утрау, Канада) Bashkir Мелвіл (востраў, Канада) Byelorussian Мелвил (остров, Канада) Bulgarian Illa de Melville (Canadà) Catalan Melville Island (pulo sa Kanada, Northwest Territories) CEB Melvillův ostrov (Ostrovy královny Alžběty) Czech
 NASA satellite photograph of Melville Island | |
 | |
| Etymology | The Viscount Melville |
|---|---|
| Geography | |
| Location | Canadian Arctic |
| Coordinates | 75°30′02″N 111°30′09″W / 75.50056°N 111.50250°W[1] |
| Archipelago | Queen Elizabeth Islands |
| Adjacent to | |
| Area | 42,149 km2 (16,274 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 33rd |
| Length | 341 km (211.9 mi) |
| Width | 210–292 km (130–181 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 762 m (2500 ft) |
| Administration | |
Canada | |
| Territories | Northwest Territories, Nunavut |
| Regions | Qikiqtaaluk, Inuvik |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 0 (uninhabited) (2024) |
Melville Island[1] (French: île Melville[citation needed]; Inuktitut: ᐃᓗᓪᓕᖅ, Ilulliq[citation needed]) is an uninhabited member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands of the Arctic Archipelago. With an area of 42,149 km2 (16,274 sq mi), it is the 33rd largest island in the world and Canada's eighth largest island.
Mountains on Melville Island, some of the largest in the western Canadian Arctic, reach heights of 750 m (2,460 ft).
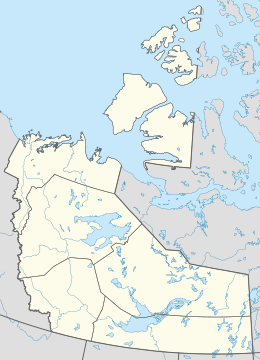
Melville Island is shared by the Northwest Territories, which is responsible for the western half of the island, and Nunavut, which is responsible for most of the eastern half. The border runs along the 110th meridian west. The eastern half of the island contains two subnational pene-exclaves that lie west of the 110th meridian and form part of the Northwest Territories. These can be reached by land only from Nunavut.
- ^ a b Coordinates are located on the NWT side. "Melville Island". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.