
Back Molibdeendisulfied Afrikaans مولیبدن دیسولفید AZB Сульфід малібдэну(IV) Byelorussian Disulfur de molibdè Catalan Sulfid molybdeničitý Czech Molybdän(IV)-sulfid German Disulfuro de molibdeno Spanish Molübdeendisulfiid Estonian مولیبدن دیسولفید Persian Molybdeenidisulfidi Finnish

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Molybdenum disulfide
| |
| Other names
Molybdenum(IV) sulfide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.877 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MoS2 | |
| Molar mass | 160.07 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black/lead-gray solid |
| Density | 5.06 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 2,375 °C (4,307 °F; 2,648 K)[4] |
| insoluble[1] | |
| Solubility | decomposed by aqua regia, hot sulfuric acid, nitric acid insoluble in dilute acids |
| Band gap | 1.23 eV (indirect, 3R or 2H bulk)[2] ~1.8 eV (direct, monolayer)[3] |
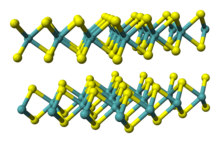
| Structure | |
| hP6, P6 3/mmc, No. 194 (2H) | |
a = 0.3161 nm (2H), 0.3163 nm (3R), c = 1.2295 nm (2H), 1.837 (3R)
| |
| Trigonal prismatic (MoIV) Pyramidal (S2−) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
62.63 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−235.10 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−225.89 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Molybdenum(IV) oxide Molybdenum diselenide Molybdenum ditelluride |
Other cations
|
Tungsten disulfide |
Related lubricants
|
Graphite |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Molybdenum disulfide (or moly) is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is MoS2.
The compound is classified as a transition metal dichalcogenide. It is a silvery black solid that occurs as the mineral molybdenite, the principal ore for molybdenum.[6] MoS2 is relatively unreactive. It is unaffected by dilute acids and oxygen. In appearance and feel, molybdenum disulfide is similar to graphite. It is widely used as a dry lubricant because of its low friction and robustness. Bulk MoS2 is a diamagnetic, indirect bandgap semiconductor similar to silicon, with a bandgap of 1.23 eV.[2]
- ^ a b Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.76. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ a b Kobayashi, K.; Yamauchi, J. (1995). "Electronic structure and scanning-tunneling-microscopy image of molybdenum dichalcogenide surfaces". Physical Review B. 51 (23): 17085–17095. Bibcode:1995PhRvB..5117085K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.51.17085. PMID 9978722.
- ^ Yun, Won Seok; Han, S. W.; Hong, Soon Cheol; Kim, In Gee; Lee, J. D. (2012). "Thickness and strain effects on electronic structures of transition metal dichalcogenides: 2H-MX2 semiconductors (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se, Te)". Physical Review B. 85 (3): 033305. Bibcode:2012PhRvB..85c3305Y. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.85.033305.
- ^ "Molybdenum Disulfide". PubChem. Retrieved August 31, 2018.
- ^ Schönfeld, B.; Huang, J. J.; Moss, S. C. (1983). "Anisotropic mean-square displacements (MSD) in single-crystals of 2H- and 3R-MoS2". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 39 (4): 404–407. Bibcode:1983AcCrB..39..404S. doi:10.1107/S0108768183002645.
- ^ Sebenik, Roger F. et al. (2005) "Molybdenum and Molybdenum Compounds", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_655