
Back ناندرولون Arabic ناندرولون AZB Нандролон Bulgarian ন্যান্ড্রোলন Bengali/Bangla Nandrolona Catalan Nandrolon Czech Nandrolon Welsh Nandrolon Danish Nandrolon German Νανδρολόνη Greek
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈnændrəloʊn/[1] |
| Trade names | • Deca-Durabolin (as ND) • Durabolin (as NPP) • Many others (see here) |
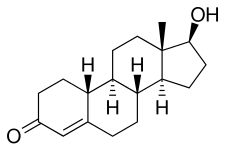
| Other names | • 19-Nortestosterone[2][3] • 10-Nortestosterone • Estr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one • Estrenolone • Oestrenolone • 19-Norandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one • Norandrostenolone[2] • Nortestrionate[2] • Nortestonate[2] • Norandroone • SG-4341[2][3] |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | • IM injection (esters) • SC injection (esters) • Eye drops (NS) |
| Drug class | Androgen; Anabolic steroid; Progestogen |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | • Oral: <3% (pigs)[5] • Intramuscular: high[6] |
| Metabolism | Liver (reduction)[7][9] |
| Metabolites | • 5α-Dihydronandrolone[7][8] • 19-Norandrosterone[7] • 19-Noretiocholanolone[7] • Conjugates[9] |
| Elimination half-life | • Nandrolone: <4.3 hours[7] • ND (IM): 6–12 days[7][8][10] • NPP: 2.7 days[10] |
| Duration of action | • ND (IM): 2–3 weeks[8][11] • NPP (IM): 5–7 days[8][10] |
| Excretion | Urine[7] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.457 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H26O2 |
| Molar mass | 274.404 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Nandrolone, also known as 19-nortestosterone, is an endogenous androgen which exists in the male body at a ratio of 1:50 compared to testosterone.[citation needed] It is also an anabolic steroid (AAS) which is medically used in the form of esters such as nandrolone decanoate (brand name Deca-Durabolin) and nandrolone phenylpropionate (brand name Durabolin).[2][12][8][13] Nandrolone esters are used in the treatment of anemias, cachexia (muscle wasting syndrome), osteoporosis, breast cancer, and for other indications.[8] They are now used by oral administration or instead are given by injection into muscle or fat.[8][13][14]
Side effects of nandrolone esters include symptoms of masculinization like acne, increased hair growth, and voice changes.[8] They are synthetic androgens and anabolic steroids and hence are agonists of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[8][15] Nandrolone has strong anabolic effects and weak androgenic effects, which give them a mild side effect profile and make them especially suitable for use in women and children.[8][15][16] There are metabolites of Nandrolone that act as long-lasting prodrugs in the body,[8] such as 5α-Dihydronandrolone.
Nandrolone esters were first described and introduced for medical use in the late 1950s.[8] They are among the most widely used anabolic steroid worldwide.[8] In addition to their medical use, nandrolone esters are used to improve physique and performance, and are said to be the most widely used anabolic steroid for such purposes.[8][17] The drugs are controlled substances in many countries and so non-medical use is generally illicit.[8]
- ^ "Nandrolone Meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary".
- ^ a b c d e f Elks J, Ganellin CR, eds. (2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. New York City: Springer. pp. 660–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. OCLC 1079003025.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
MortonHall2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-15.
- ^ McEvoy JD, McVeigh CE, McCaughey WJ (December 1998). "Residues of nortestosterone esters at injection sites. Part 1. Oral bioavailability". The Analyst. 123 (12): 2475–8. doi:10.1039/a804919j. PMID 10435281.
- ^ Becker KL (2001). Principles and Practice of Endocrinology and Metabolism. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1185–. ISBN 978-0-7817-1750-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Deca-Durabolin" (PDF). Schering-Plough. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Llewellyn W (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 402–412, 460–467, 193–194. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- ^ a b Thomas JA (6 December 2012). Drugs, Athletes, and Physical Performance. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 27–29. ISBN 978-1-4684-5499-4.
- ^ a b c Minto CF, Howe C, Wishart S, Conway AJ, Handelsman DJ (April 1997). "Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nandrolone esters in oil vehicle: effects of ester, injection site and injection volume". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 281 (1): 93–102. PMID 9103484.
- ^ "Deca-Durabolin" (PDF). Merck Sharp & Dohme (Australia).
- ^ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 716–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b Sneader W (23 June 2005). Drug Discovery: A History. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 206–. ISBN 978-0-471-89979-2.
- ^ Singh GK, Turner L, Desai R, Jimenez M, Handelsman DJ (July 2014). "Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study of subcutaneous injection of depot nandrolone decanoate using dried blood spots sampling coupled with ultrapressure liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assays". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 99 (7): 2592–8. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-1243. PMID 24684468.
- ^ a b Kicman AT (June 2008). "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 502–21. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. PMC 2439524. PMID 18500378.
- ^ Kochakian CD (6 December 2012). Anabolic-Androgenic Steroids. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 401–. ISBN 978-3-642-66353-6.
- ^ Jameson JL, De Groot LJ (25 February 2015). Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 2388–. ISBN 978-0-323-32195-2.