
Back Oktaedergruppe German Okedra simetrio Esperanto Simetría octaédrica Spanish Oktaedrinen symmetria Finnish Simetri oktahedral ID 정팔면체 대칭 Korean Simetrie octaedrică Romanian Oktaedrska simetrija Slovenian
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (May 2013) |
 Involutional symmetry Cs, (*) [ ] = |
 Cyclic symmetry Cnv, (*nn) [n] = |
 Dihedral symmetry Dnh, (*n22) [n,2] = | |
| Polyhedral group, [n,3], (*n32) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Tetrahedral symmetry Td, (*332) [3,3] = |
 Octahedral symmetry Oh, (*432) [4,3] = |
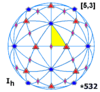 Icosahedral symmetry Ih, (*532) [5,3] = | |

The four hexagonal cycles have the inversion (the black knot on top) in common. The hexagons are symmetric, so e.g. 3 and 4 are in the same cycle.
A regular octahedron has 24 rotational (or orientation-preserving) symmetries, and 48 symmetries altogether. These include transformations that combine a reflection and a rotation. A cube has the same set of symmetries, since it is the polyhedron that is dual to an octahedron.
The group of orientation-preserving symmetries is S4, the symmetric group or the group of permutations of four objects, since there is exactly one such symmetry for each permutation of the four diagonals of the cube.