
Back أورملوكسيفين Arabic ഓർമെലോക്സിഫെൻ Malayalam Ormeloxifeno Portuguese Ormeloksifen Serbo-Croatian Ormeloksifen Serbian Ormeloksifen Turkish Ormeloxifene Vietnamese
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Centron, Novex-DS, Saheli, Sevista, Chhaya |
| Other names | Centchroman |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Selective estrogen receptor modulator |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 7 days |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
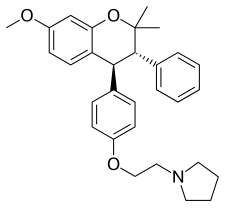
| Formula | C30H35NO3 |
| Molar mass | 457.614 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
| Ormeloxifene | |
|---|---|
| Background | |
| Type | Antiestrogen |
| First use | 1991 |
| Failure rates (first year) | |
| Perfect use | 2% |
| Typical use | 9% |
| Usage | |
| Duration effect | One week |
| Reversibility | Immediate |
| User reminders | Taken twice weekly for first 13 weeks |
| Clinic review | Annually |
| Advantages and disadvantages | |
| STI protection | No |
| Periods | May disrupt |
| Safe while breastfeeding | Yes[1] |
| Weight | No proven effect |
| Benefits | Non hormonal |
| Risks | Delayed menstruation |
| Medical notes | |
| Only approved as a contraceptive in India | |
Ormeloxifene, also known as centchroman, is one of the selective estrogen receptor modulators,[2] or SERMs, a class of medication which acts on the estrogen receptor. It is best known as a nonsteroidal oral contraceptive which is taken once per week. In India, ormeloxifene has been available as birth control since the early 1990s, and it was marketed there under the trade name Saheli,[3] currently available free-of-cost for the women in India as Chhaya (Centchroman).[4][5]
Ormeloxifene has also been licensed under the trade names Ormalin, Novex-DS, Centron, and Sevista.
- ^ Gupta RC, Paliwal JK, Nityanand S, Asthana OP, Lal J (November 1995). "Centchroman: a new non-steroidal oral contraceptive in human milk". Contraception. 52 (5): 301–305. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(95)00214-U. PMID 8585887.
- ^ Makker A, Tandon I, Goel MM, Singh M, Singh MM (June 2009). "Effect of ormeloxifene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, on biomarkers of endometrial receptivity and pinopode development and its relation to fertility and infertility in Indian subjects". Fertility and Sterility. 91 (6): 2298–2307. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.04.018. PMID 18675966.
- ^ "HLL - Product Overview". Archived from the original on 1 November 2018.
- ^ "Chhaya". Centre for Health Informatics (CHI) of the National Health Portal (NHP), by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW). Government of India. Archived from the original on 11 May 2021. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- ^ "Contraception and women's empowerment: Here's how safe, reliable contraceptives are freeing women to earn". Hindustan Times. 10 July 2018. Retrieved 29 June 2020.