
Back التهاب العظام الليفي الكيسي Arabic Ostitis fibrosa cystica German Osteítis fibrosa Spanish Osteitis fibrosa sistika ID Dystrofia kości przytarczyczkowa Polish Doença de von Recklinghausen Portuguese Fibroznocistični osteitis Slovenian
| Osteitis fibrosa cystica | |
|---|---|
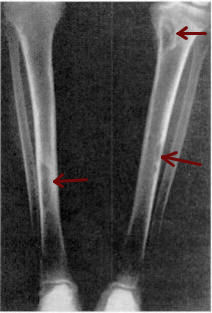 | |
| Osteitis fibrosa cystica of the tibia. Arrows point to the brown tumors which are typically present in bones of people with OFC. | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
| Symptoms | bone pain or tenderness, bone fractures, and skeletal deformities |
| Causes | hyperparathyroidism |
Osteitis fibrosa cystica (/ˌɒstiˈaɪtɪs faɪˈbroʊsə ˈsɪstɪkə/ OSS-tee-EYE-tis fy-BROH-sə SIS-tik-ə) is a skeletal disorder resulting in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue (peritrabecular fibrosis), and the formation of cyst-like brown tumors in and around the bone. Osteitis fibrosis cystica (OFC), also known as osteitis fibrosa, osteodystrophia fibrosa, and von Recklinghausen's disease of bone (not to be confused with von Recklinghausen's disease, neurofibromatosis type I), is caused by hyperparathyroidism, which is a surplus of parathyroid hormone from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy. Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium, from the bone into the bloodstream, causing both elevated blood calcium levels, and the structural changes which weaken the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss.
First described in the nineteenth century, OFC is currently detected through a combination of blood testing, X-rays, and tissue sampling. Before 1950, around half of those diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism in the United States saw it progress to OFC, but with early identification techniques and improved treatment methods, instances of OFC in developed countries are increasingly rare. Where treatment is required, it normally involves addressing the underlying hyperparathyroidism before commencing long-term treatment for OFC—depending on its cause and severity, this can range from hydration and exercise to surgical intervention.