
Back পরিক্রমা Bengali/Bangla Pradakshina German Parikrama French પરિક્રમા Gujarati פראדקשינה HE परिक्रमा Hindi Pradaksina ID Pradakṣiṇā Italian 右繞 Japanese ಪ್ರದಕ್ಷಿಣೆ Kannada

Parikrama or Pradakshina is clockwise circumambulation of sacred entities, and the path along which this is performed, as practiced in the Indic religions – Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism.[1][2][3][4][5] In Buddhism, it refers only to the path along which this is performed.[3] In Indic religions, the parikrama is typically done after completion of traditional worship (puja) and after paying homage to the deity. Parikrama must be done with dhyāna (spiritual contemplation and meditation).
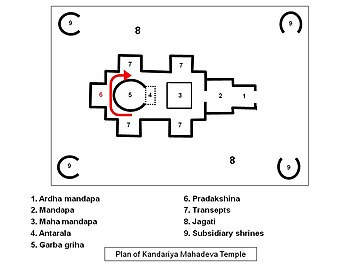

In Hinduism, parikrama of religious deities in a temple, sacred rivers, sacred hills and a close cluster of temples as a symbol of prayer is an integral part of Hindu worship.[3][6][7] Hindu temple architecture include various Pradakshina paths.[8] There could a parikrama path surrounding the chief deity and several other broader paths concentric to the main path, although it is not uncommon to find non-concentric parikrama paths. At times the outermost parikrama path covers the whole village, town, city, thereby implying that the length of the path can stretch.[6][9] Parikrama is also done around the sacred Peepal tree, tulsi (Indian basil plant), and agni (sacred fire or the fire God),[10][11] and agni parikrama, known as Mangal phera, is a part of the Hindu wedding ceremony.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ds2002was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Linda Kay Davidson; David Martin Gitlitz (2002). Pilgrimage: From the Ganges to Graceland : an Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. p. 113. ISBN 978-1-57607-004-8.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Bowkerwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cort, John (2011). Jains in the world : religious values and ideology in India. New York Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-19-979664-9.
- ^ Pashaura Singh and Louis Fenech (2014). The Oxford handbook of Sikh studies. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. p. 439. ISBN 978-0-19-969930-8.
- ^ a b http://www.hindunet.org/faq/fom-serv/cache/31.html Archived 2017-01-15 at the Wayback Machine Why do we perform Pradakshina or Parikrama?
- ^ http://www.hinduism.co.za/kaabaa.htm Kaaba a Hindu Temple?Hindus invariably circumambulate around their deities
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
hin1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Architecture of the Indian Subcontinent – glossary". indoarch.org. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ^ http://www.kamat.com/indica/culture/sub-cultures/pradakshina.htm The Concept of Pradaksina
- ^ "Darbashayanam". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2008-10-20.