
Back پیپرین AZB পাইপেরিন Bengali/Bangla Piperin BS Piperin German Piperino Esperanto Piperina Spanish Piperina Basque پیپرین Persian Piperiini Finnish Pipérine French
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
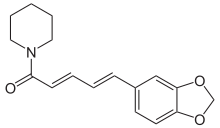
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E,4E)-5-(2H-1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one | |
| Other names
(2E,4E)-5-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1-(piperidin-1-yl)penta-2,4-dien-1-one
Piperoylpiperidine Bioperine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.135 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H19NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 285.343 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.193 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 130 °C (266 °F; 403 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| 40 mg/l | |
| Solubility in ethanol | soluble |
| Solubility in chloroform | 1 g/1.7 ml |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS for piperine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
| Piperine | |
|---|---|
| Scoville scale | 150,000[1] SHU |
Piperine, possibly along with its isomer chavicine,[2] is the compound[3] responsible for the pungency of black pepper and long pepper. It has been used in some forms of traditional medicine.[4]
- ^ Mangathayaru, K. (2013). Pharmacognosy: An Indian perspective. Pearson Education India. p. 274. ISBN 9789332520264.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
De_Cleyn&Verzele1972was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (11th ed.), Merck, 1989, p. 7442, ISBN 091191028X
- ^ Srinivasan, K. (2007). "Black pepper and its pungent principle-piperine: A review of diverse physiological effects". Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 47 (8): 735–748. doi:10.1080/10408390601062054. PMID 17987447. S2CID 42908718.