Back Prins-Edward-eiland Afrikaans ፕርንስ ኤድወርድ አይለንድ Amharic Eadweardes Æþelinges Iegland ANG جزيرة الأمير إدوارد Arabic ܓܙܪܬܐ ܕܐܡܝܪܐ ܐܕܘܐܪܕ ARC Islla del Príncipe Dubardu AST प्रिन्स एड्वर्ड द्वीप AWA Şahzadə Eduard Adası Azerbaijani پرنس ادوارد آداسی AZB Pulo Rajaputra Edward BAN
Prince Edward Island
| |
|---|---|
| Motto(s): | |
| Coordinates: 46°24′N 63°12′W / 46.400°N 63.200°W[2] | |
| Country | Canada |
| Confederation | July 1, 1873 (8th) |
| Capital (and largest city) | Charlottetown |
| Largest metro | Charlottetown |
| Government | |
| • Type | Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| • Lieutenant Governor | Wassim Salamoun |
| • Premier | Dennis King |
| Legislature | Legislative Assembly of Prince Edward Island |
| Federal representation | Parliament of Canada |
| House seats | 4 of 338 (1.2%) |
| Senate seats | 4 of 105 (3.8%) |
| Area | |
• Total | 5,660 km2 (2,190 sq mi) |
| • Land | 5,660 km2 (2,190 sq mi) |
| • Water | 0 km2 (0 sq mi) 0% |
| • Rank | 13th |
| 0.1% of Canada | |
| Population (2021) | |
• Total | 154,331[3] |
• Estimate (Q4 2024) | 179,301[5] |
| • Rank | 10th |
| • Density | 27.27/km2 (70.6/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Prince Edward Islander, Islander, PEIer |
| Official languages | English (de facto)[6] |
| GDP | |
| • Rank | 10th |
| • Total (2017) | 6.652 billion |
| • Per capita | C$36,740 (13th) |
| HDI | |
| • HDI (2021) | 0.930[7] — Very high (4th) |
| Time zone | UTC-04:00 (Atlantic) |
| Canadian postal abbr. | PE |
| Postal code prefix | |
| ISO 3166 code | CA-PE |
| Flower | Pink lady's slipper |
| Tree | Red oak |
| Bird | Blue jay |
| Rankings include all provinces and territories | |
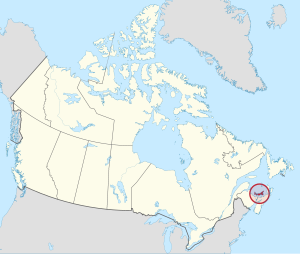
Prince Edward Island[a] is an island province of Canada. While it is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation".[8] Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces.
Part of the traditional lands of the Mi'kmaq, it was colonized by the French in 1604 as part of the colony of Acadia. The island, known as Isle St-Jean (St. John's Island), was ceded to the British at the conclusion of the Seven Years' War in 1763 and became part of the colony of Nova Scotia. In 1769, St. John's island became its own British colony and its name was changed to Prince Edward Island (PEI) in 1798. PEI hosted the Charlottetown Conference in 1864 to discuss a union of the Maritime provinces; however, the conference became the first in a series of meetings which led to Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867. Prince Edward Island initially balked at Confederation but, facing bankruptcy from the Land Question and construction of a railroad, joined as Canada's seventh province on July 1, 1873.
According to Statistics Canada, the province of Prince Edward Island had 179,301 residents in 2024.[9] The backbone of the island economy is farming; it produces 25% of Canada's potatoes. Other important industries include fisheries, tourism, aerospace, biotechnology, information technology and renewable energy.[10] As Prince Edward Island is one of Canada's older settled areas, its population still reflects the origins of its earliest settlers, with Acadian, Scottish, Irish, and English surnames being dominant.
Prince Edward Island is located in the Gulf of St. Lawrence, about 10 km (6 miles) across the Northumberland Strait from both Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. It is about 200 kilometres (120 miles) north of Halifax and 600 kilometres (370 miles) east of Quebec City. It has a land area of 5,686.03 km2 (2,195.39 sq mi),[11] is the 104th-largest island in the world and Canada's 23rd-largest island. It is the only Canadian province consisting entirely of islands.
- ^ Government of Canada, Natural Resources Canada. "Place names - Île-du-Prince-Édouard". www4.rncan.gc.ca. Archived from the original on December 17, 2019. Retrieved November 15, 2021.
- ^ "Prince Edward Island". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts: Canada, provinces and territories". Statistics Canada. February 9, 2022. Archived from the original on February 9, 2022. Retrieved February 9, 2022.
- ^ "Land and freshwater area, by province and territory". Statistics Canada. February 1, 2005. Archived from the original on October 19, 2012. Retrieved August 5, 2012.
- ^ "Population estimates, quarterly". Statistics Canada. September 27, 2023. Archived from the original on September 28, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2023.
- ^ "The Legal Context of Canada's Official Languages". University of Ottawa. Archived from the original on October 10, 2017. Retrieved March 7, 2019.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Subnational HDI". Global Data Lab. Archived from the original on September 25, 2021. Retrieved September 6, 2021.
- ^ Prince Edward Island. Britannica Concise Encyclopedia. 2013. Archived from the original on July 28, 2020. Retrieved September 30, 2013.
- ^ "PEI Population Report Quarterly prepared by PEI Statistics Bureau". Government of Prince Edward Island. Government of Canada, Statistics Canada. June 19, 2019. Archived from the original on June 18, 2019. Retrieved June 19, 2019.
- ^ Toolkit, Web Experience (January 9, 2018). "Island Economy". Princeedwardisland.ca. Archived from the original on July 2, 2019. Retrieved July 2, 2019.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts, for Canada, provinces and territories, 2016 and 2011 censuses". Statistics Canada. February 6, 2017. Archived from the original on October 12, 2017. Retrieved May 8, 2017.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).