
Back Medias pitagóricas Spanish Batezbesteko pitagoratar Basque میانگینهای فیثاغورثی Persian Pythagoraan keskiarvo Finnish Moyenne pythagoricienne French ピタゴラス平均 Japanese មធ្យមពីតាករ Cambodian 피타고라스 평균 Korean Pitagoro vidurkiai Lithuanian பித்தாகரசின் சராசரிகள் Tamil
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2019) |

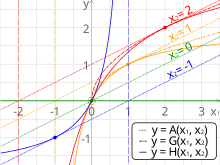
In mathematics, the three classical Pythagorean means are the arithmetic mean (AM), the geometric mean (GM), and the harmonic mean (HM). These means were studied with proportions by Pythagoreans and later generations of Greek mathematicians[1] because of their importance in geometry and music.
- ^ Heath, Thomas. History of Ancient Greek Mathematics.