
Back Vorgehängte hinterlüftete Fassade German Koolaus Finnish Ventilirana fasada Croatian Facciata ventilata Italian Facciada ventilada LMO Вентилируемый фасад Russian Havalandırmalı giydirme cephe Turkish Навісний вентильований фасад Ukrainian
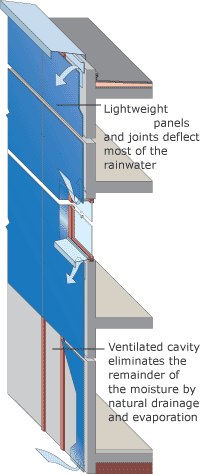

A rainscreen is an exterior wall detail where the siding (wall cladding) stands off from the moisture-resistant surface of an air/water barrier applied to the sheathing to create a capillary break and to allow drainage and evaporation. The rainscreen is the cladding or siding itself[1] but the term rainscreen implies a system of building. Ideally the rainscreen prevents the wall air/water barrier from getting wet but because of cladding attachments and penetrations (such as windows and doors) water is likely to reach this point, and hence materials are selected to be moisture tolerant and integrated with flashing. In some cases a rainscreen wall is called a pressure-equalized rainscreen wall where the ventilation openings are large enough for the air pressure to nearly equalize on both sides of the rain screen,[2] but this name has been criticized as being redundant[3] and is only useful to scientists and engineers.
- ^ Micheal J. Lough and David Altenhofen, "The Rain Screen Principle" Archived 2014-03-22 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Brown, W. C, Rousseau, M. Z., and Dalgliesh, W. A., "Field Testing of Pressure-Equalized Rain Screen Walls," Donaldson, Barry, ed.. Exterior wall systems: glass and concrete technology, design, and construction. Philadelphia, PA: ASTM, 1991. 59. Print.
- ^ Rousseau, M.Z., "Facts and Fictions of Rain-Screen Walls", Construction Canada, 1990.