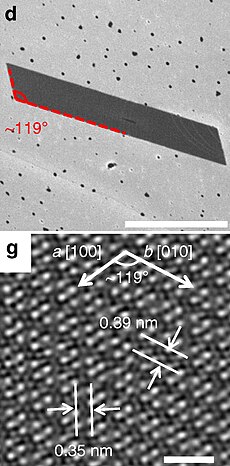
 d: SEM micrograph of a typical parallelogram-shaped ReSe2 flake, scale bar 1 µm.
g: top view of the ReSe2 atomic lattice | |
 Unit cell of rhenium diselenide.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bis(selanylidene)rhenium
| |
| Other names
Rhenium(IV) selenide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.696 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ReSe2 | |
| Molar mass | 344.13 g/mol[1] |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 9.22 g/cm3[2] |
| insoluble | |
| Band gap | ~1.2 eV (300 K), indirect[3] |
| Structure | |
| Triclinic, aP12, space group P1, No 2[2] | |
a = 0.6602 nm, b = 0.6716 nm, c = 0.6728 nm α = 91.82°, β = 104.9°, γ = 118.94°
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Rhenium(IV) oxide Rhenium disulfide Rhenium ditelluride |
Other cations
|
Manganese diselenide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rhenium diselenide is an inorganic compound with the formula ReSe2. It has a layered structure where atoms are strongly bonded within each layer. The layers are held together by weak Van der Waals bonds, and can be easily peeled off from the bulk material.
- ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.84. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ a b Wildervanck, J.C; Jellinek, F (1971). "The dichalcogenides of technetium and rhenium". Journal of the Less Common Metals. 24: 73–81. doi:10.1016/0022-5088(71)90168-8.
- ^ Dumcenco, D; Huang, Y. S; Liang, C. H; Tiong, K. K (2008). "Optical characterization of Au-doped rhenium diselenide single crystals". Journal of Applied Physics. 104 (6): 063501–063501–6. Bibcode:2008JAP...104f3501D. doi:10.1063/1.2977682.
