
Back Sea Cat (ЗРК) Bulgarian Sea Cat Czech Seacat German Sea Cat Spanish Sea Cat Finnish Sea Cat Italian シーキャット (ミサイル) Japanese Peluru berpandu Sea Cat Malay Sea Cat Dutch Sea Cat Polish
| Seacat | |
|---|---|
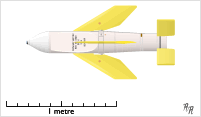 Seacat GWS-20 series missile | |
| Type | Surface-to-air missile |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1962–present |
| Used by | See operators |
| Wars | 1971 Indo-Pakistani War Iran–Iraq War Falklands War South African Border War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Short Brothers |
| Manufacturer | Short Brothers |
| Variants | See variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 68 kg (150 lb) |
| Length | 1.48 m (58 in) |
| Diameter | 0.22 m (8.7 in) |
| Wingspan | 0.70 m (28 in) |
| Warhead | 40 lb (18 kg) continuous-rod warhead |
Detonation mechanism | Proximity |
| Engine | 2 stage motor |
Operational range | 500–5,000 m (1,600–16,400 ft) or more |
| Maximum speed | Mach 0.8 |
Guidance system | CLOS and radio link |
Steering system | Control surfaces |
Launch platform | Ship |
Seacat was a British short-range surface-to-air missile system intended to replace the ubiquitous Bofors 40 mm gun aboard warships of all sizes. It was the world's first operational shipboard point-defence missile system, and was designed so that the Bofors guns could be replaced with minimum modification to the recipient vessel and (originally) using existing fire-control systems. A mobile land-based version of the system was known as Tigercat.
The initial GWS.20 version was manually controlled, in keeping with the need for a rapidly developed and deployed system. Several variants followed; GWS.21 added radar-cued manual control for night and bad-weather use, GWS.22 added a SACLOS automatic guidance mode, and the final GWS.24 had fully automatic engagement. Tigercat saw relatively brief service before being replaced in British service by the Rapier, while Seacat saw longer service until being replaced by Sea Wolf and newer technology close-in weapons systems.
Seacat and Tigercat were both successful in the export market and some remain in service.