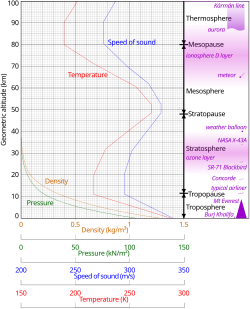
The U.S. Standard Atmosphere is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. The model, based on an existing international standard, was first published in 1958 by the U.S. Committee on Extension to the Standard Atmosphere, and was updated in 1962, 1966, and 1976. It is largely consistent in methodology with the International Standard Atmosphere, differing mainly in the assumed temperature distribution at higher altitudes.

