
Back Vaatbundel Afrikaans حزمة وعائية Arabic Праводзячы пучок Byelorussian ভাস্কুলার বান্ডল Bengali/Bangla Provodno tkivo BS Cévní svazek Czech Leitbündel German Vaskulaj faskoj Esperanto Haz vascular Spanish دستههای آوندی Persian
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (February 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|

(black: Xylem, green: Phloem, white: Cambium)
A concentric, periphloematic(Hadrocentric)
B concentric, perixylematic(Leptocentric)
C radial with inner xylem, here with four xylem-poles, left closed, right open
D collateral closed
E collateral open
F bicollateral open



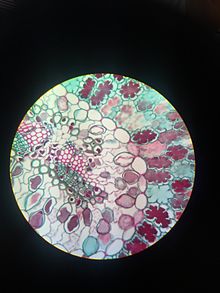
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will include supporting and protective tissues. There is also a tissue between xylem and phloem, which is the cambium.
The xylem typically lies towards the axis (adaxial) with phloem positioned away from the axis (abaxial). In a stem or root this means that the xylem is closer to the centre of the stem or root while the phloem is closer to the exterior. In a leaf, the adaxial surface of the leaf will usually be the upper side, with the abaxial surface the lower side.
The sugars synthesized by the plant with sun light are transported by the phloem, which is closer to the lower surface. Aphids and leaf hoppers feed off of these sugars by tapping into the phloem. This is why aphids and leaf hoppers are typically found on the underside of a leaf rather than on the top. The position of vascular bundles relative to each other may vary considerably: see stele. The vascular bundle are depend on size of veins
