
Back Conseil législatif d'Australie-Occidentale French Rada Ustawodawcza Australii Zachodniej Polish Western Australian Legislative Council SIMPLE
Legislative Council | |
|---|---|
| 41st Parliament | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| History | |
| Founded | 7 February 1832 |
| Leadership | |
Chair of Committees | |
Leader of the Government | |
Deputy Leader of the Government | |
Government Whip | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 36 |
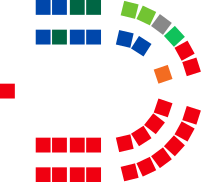 | |
Political groups | Government (21) Labor (21) |
Length of term | 4 years |
| Elections | |
| Single transferable vote | |
Last election | 13 March 2021 |
Next election | 8 March 2025 |
| Meeting place | |
| Legislative Council Chamber Parliament House, Perth Western Australia, Australia | |
| Website | |
| WA Legislative Council | |
The Western Australian Legislative Council is the upper house of the Parliament of Western Australia, a state of Australia. It is regarded as a house of review for legislation passed by the Legislative Assembly, the lower house. The two Houses of Parliament sit in Parliament House in the state capital, Perth.
Effective on 20 May 2005, for the election of members of the Legislative Council, the state was divided into six electoral regions by community of interest – three metropolitan and three rural – each electing six members to the Legislative Council.[1][2] The 2005 changes continued to maintain the previous malapportionment in favour of rural regions. Legislation was passed in 2021 to abolish these regions and increase the size of the council to 37 seats, all of which will be elected by the state-at-large. The changes will take effect in the 2025 state election.[3][4][5][6]
Since 2008, the Legislative Council has had 36 members. Since the 2013 state election, both houses of Parliament have had fixed four-year terms, with elections being held every four years on the second Saturday in March,[7][8] though the term of the Legislative Council not expiring until May after the election. In the current Legislative Council, elected at the 2021 election, Labor has majority control of the chamber—the first time any party gained the majority in the upper house since 1983.[9]
Until 2021, six members of the Legislative Council are elected from each of the six regions under a proportional and preferential voting system using the single transferable vote method. Each council region overlaps with a varying number of Assembly seats. Because of the proportional representation system in place as well as the malapportionment in favour of rural regions, the Legislative Council has traditionally been controlled by a coalition of the Liberal and National parties, and minor parties and independents have been more easily elected.[10]
From the 2025 election, the proportional and preferential voting system of the single transferable vote will be retained for the chamber. The six regions used as districts for the election of councillors has been abolished. Instead the 36 seats will be elected from one state-wide seat. This removes the malapportionment which favoured the National Party, which often generated a Coalition majority in the state's upper House. Using a state-wide voting system, like as is done in New South Wales, lowers the threshold for entry to the chamber to below 3% of the state-wide vote after preferences, thus favouring minor parties and independents[11].
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Election of the Legislative Council on website of Parliament of Western Australia
- ^ Electoral Amendment and Repeal Act 2005 (WA) s 4.
- ^ Rhiannon Shine and Jacob Kagi (15 September 2021). "Mark McGowan announces sweeping changes to WA's electoral system, abolishing regions". ABC News.
- ^ "Progress of Bills: Constitutional and Electoral Legislation Amendment (Electoral Equality) Bill 2021". parliament.wa.gov.au.
- ^ "WA government uses majority to introduce sweeping changes to electoral system". ABC News. 17 November 2021.
- ^ "Constitutional and Electoral Legislation Amendment (Electoral Equality) Act 2021" (PDF). legislation.wa.gov.au.
- ^ "New laws fix state election dates". Abc.net.au. 3 November 2011. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- ^ Antony Green (8 February 2011). "Future election dates". Blogs.abc.net.au. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- ^ ABC News, Legislative Council results
- ^ Parliament of Western Australia, Election of the Legislative Council
- ^ Green, Antony; Analyst, ABC Chief Election. "Election Preview". abc.net.au. Retrieved 18 January 2025.