
Back كورتيزول Arabic Kortizol Azerbaijani کورتیزول AZB Кортизол Bulgarian কর্টিসল Bengali/Bangla Kortizol BS Cortisol Catalan کۆرتیزۆڵ CKB Kortizol Czech Кортизол CV
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Nama sistematis (IUPAC) | |
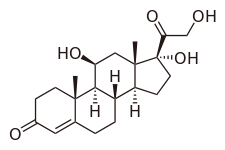
| (11β)-11,17,21-trihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione | |
| Data klinis | |
| Kat. kehamilan | C |
| Status hukum | Rx Only (U.S.) (excluding 1-2% strength topical) |
| Rute | Oral tablets, intravenously, topical |
| Pengenal | |
| Nomor CAS | 50-23-7 |
| Kode ATC | H02AB09 (and others) |
| PubChem | CID 5754 |
| ChemSpider | 5551 |
| UNII | WI4X0X7BPJ |
| KEGG | D00088 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL389621 |
| Data kimia | |
| Rumus | C21H30O5 |
| Massa mol. | 362.460 |
| SMILES | eMolecules & PubChem |
| |
Kortisol (bahasa Inggris: cortisol, hydrocortisone, 11beta,17alpha,21-trihydroxy-4-pregnene-3,20-dione) adalah hormon steroid dari golongan glukokortikoid yang diproduksi oleh sel di dalam zona fasikulata pada kelenjar adrenal[1] sebagai respon terhadap stimulasi hormon ACTH yang disekresi oleh kelenjar hipofisis, juga merupakan hasil reaksi organik hidrogenasi pada gugus 11-keto[2] molekul hormon kortison yang dikatalis oleh enzim 11β-hidroksisteroid dehidrogenase tipe 1 yang umumnya disekresi oleh jaringan adiposa. kelebihan hormon ini dalam darah menyebabkan sindrom cushing [3] Selain itu, hormon kortisol juga diproduksi oleh hati.[4]
Hormon ini bekerja dengan meningkatkan kadar gula darah melalui mekanisme glukoneogenesis, menekan kerja sistem imun, dan meningkatkan metabolisme lemak, protein, dan karbohidrat.[5] Selain itu, hormon ini juga menghambat pembentukan tulang.[6]
Hidroksikortison adalah nama lain dari kortisol yang digunakan dalam pengobatan. Hidroksikortison digunakan untuk mengobati kekurangan produksi kortisol di dalam tubuh.
- ^ (Inggris) "Medical Biochemistry Page". Michael W. King. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 2010-11-28. Diakses tanggal 2011-04-28.
- ^ (Inggris) "Cortisol vs. corticosterone". Theophilus Samuels. Diakses tanggal 2011-04-28.
- ^ (Inggris) "Cortisol Release From Adipose Tissue by 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 in Humans". Endocrinology Unit, University of Edinburgh, Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine, Umeå University Hospital, Department of Radiology, Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, Oxford Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism and NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, University of Oxford, Liver Unit, Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh; Roland H. Stimson, Jonas Andersson, Ruth Andrew, Doris N. Redhead, Fredrik Karpe,4 Peter C. Hayes, Tommy Olsson, Brian R. Walker. Diakses tanggal 2011-04-28.
- ^ (Inggris) "Liver Is the Site of Splanchnic Cortisol Production in Obese Nondiabetic Humans". Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, Metabolism, and Nutrition, Department of Radiology, Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Department of Surgery, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Global Pharmaceutical Research and Development, Abbott Laboratories; Rita Basu, Ananda Basu, Meagan Grudzien, Paul Jung, Peer Jacobson, Michael Johnson, Ravinder Singh, Michael Sarr, dan Robert A. Rizza1. Diakses tanggal 2011-04-28.
In contrast, the liver produced both cortisol (22.7 ± 3.90 μg/min) and D3 cortisol (1.9 ± 0.4 μg/min)...
- ^ (Inggris)Hoehn K, Marieb EN (2010). Human Anatomy & Physiology. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings.ISBN 0-321-60261-7.
- ^ (Inggris)Chyun YS, Kream BE, Raisz LG (1984). "Cortisol decreases bone formation by inhibiting periosteal cell proliferation". Endocrinology 114 (2): 477–80.doi:10.1210/endo-114-2-477. PMID 6690287.