
Back Arktik ACE Noordpoolgebied Afrikaans Arktis ALS አርክቲክ Amharic Norða ANG المنطقة القطبية الشمالية Arabic اركتيك ARZ Árticu AST Арктика AV Arktika Azerbaijani
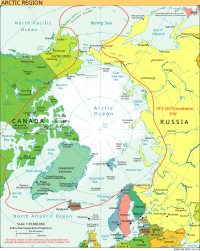
The Arctic is the area around the Earth's North Pole. The Arctic includes parts of Russia, Alaska, Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Lapland and Svalbard as well as the Arctic Ocean. It is an ocean, mostly covered with ice. Most scientists call the area north of the treeline Arctic. Trees will not grow when the temperatures get too cold. The forests of the continents end in the far north or high up a mountain. The place where in the trees stop is called the tree line.[1]
The area north of the treeline is not an empty ice field. In fact, the only large ice-covered land is central Greenland, which is covered year-round by a continental glacier. The land of the Arctic is around the edges of the Arctic Circle and is usually covered with tundra. A tundra is a cold, almost treeless plain covered with moss and sedges (grasslike plants).
Tundras get little rain or snow. However, they are very wet in the summer time because, three feet (1m) or so below the surface, the ground is always frozen. This permafrost is a layer of ice with the hardness of stone that keeps water from soaking into the earth beneath it. Permafrost can be thousands of feet thick. In the summer the ground on top thaws out when the sun shines and the snow that did fall melts. But the melted snow cannot drain into the ground; it just soaks the topsoil. There is no place for the water to go, except to form lakes and puddles on top of the ground until it freezes again or dries up.
In the Arctic, during summer there are nights when the Sun never sets. This is because during summer there, the North Pole points toward the Sun. So, sometimes people call it the Land of the Midnight Sun.
The word 'Arctic' comes from the Greek word αρκτος, meaning "bear". The North Pole aims at the stars called the Great Bear and the Little Bear.
- ↑ Theresa K. Buskey (March 2001). LIFEPAC History and Geography. Alpha Omega Publications. pp. 18 to 19. ISBN 978-1-58095-155-5.