Back تنفس خلوي Arabic Тканкавае дыханне Byelorussian Клетъчно дишане Bulgarian সবাত শ্বসন Bengali/Bangla Analadur Breton Ćelijsko disanje BS Respiració cel·lular Catalan خانە ھەناسە CKB Buněčné dýchání Czech Resbiradaeth cellog Welsh
Cellular respiration is what cells do to break up sugars to get energy they can use. Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create ATP, a chemical which the cell uses for energy.
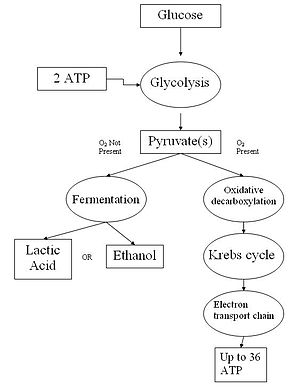
Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration. It has four stages known as glycolysis, Link reaction, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. This produces ATP which supplies the energy that cells need to do work.
When they do not get enough oxygen, the cells use anaerobic respiration, which does not use oxygen. However, this process produces lactic acid, and is not as efficient as when oxygen is used.
Aerobic respiration, the process that does use oxygen, produces much more energy and does not produce lactic acid. It also produces carbon dioxide as a waste product, which then enters the circulatory system. The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs, where it is exchanged for oxygen.
The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is:
The word equation for this is:
Aerobic cellular respiration has four stages. Each is important, and could not happen without the one before it. The steps of aerobic cellular respiration are:
- Glycolysis (the break down of glucose)
- Link reaction
- Krebs cycle
- Electron transport chain, or ETC