
Back Nederlands Afrikaans Niederländische Sprache ALS ሆላንድኛ Amharic Idioma neerlandés AN Niðerlendisc sprǣc ANG डच भाषा ANP اللغة الهولندية Arabic ܠܫܢܐ ܗܘܠܢܕܝܐ ARC لهولاندية ARY نيديرلاندى ARZ
| Dutch | |
|---|---|
| Nederlands | |
| Pronunciation | [ˈneːdərlɑnts] ( |
| Native to | Netherlands and Flanders |
| Region | Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname; also in Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten, French Flanders |
| Ethnicity | |
Native speakers | 22 million (2016)[1] Total (L1 plus L2 speakers): 28 million (2018)[2] |
Early forms | |
| Signed Dutch (NmG) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
|
| Regulated by | Nederlandse Taalunie (Dutch Language Union) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | nl |
| ISO 639-2 | dut (B) nld (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | nld Dutch/Flemish |
| Glottolog | mode1257 |
| Linguasphere | 52-ACB-a |
 Dutch-speaking world (included are areas of daughter-language Afrikaans) | |
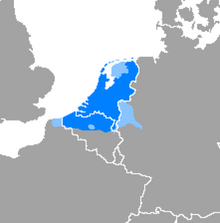 Distribution of the Dutch language and its dialects in Western Europe | |
Dutch (Dutch: Nederlands) is a West Germanic language. It comes from the Netherlands and is the country's official language.[3] It is also spoken in the northern half of Belgium (the region called Flanders), and in the South American country of Suriname. A language known as Afrikaans was developed from Dutch by the people in southern Africa and is now spoken mainly in South Africa but also in nearby Namibia. About 22 million people around the world speak Dutch.[4]
- ↑ Dutch at Ethnologue (19th ed., 2016)
- ↑ "Dutch". Languages at Leicester. University of Leicester. Archived from the original on 2014-05-02.
- ↑ "Language". I Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 6 October 2015. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- ↑ Wayne C. Thompson, Western Europe 2015-2016 (Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield, 2015), p. 201