
Back Амаџьар бызшәа Abkhazian Hongaars Afrikaans Ungarische Sprache ALS ሀንጋርኛ Amharic Idioma hongaro AN हंगेरियन भाषा ANP اللغة المجرية Arabic لهنݣارية ARY لغه مجرى ARZ Idioma húngaru AST
| Hungarian | |
|---|---|
| magyar | |
| Native to | Hungary and areas of Austria, Croatia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Ukraine |
Native speakers | 14–15 million (2005)[1] |
| Latin (Hungarian alphabet) Hungarian Braille | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Research Institute for Linguistics of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | hu |
| ISO 639-2 | hun |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:hun – Modern Hungarianohu – Old Hungarian |
ohu Old Hungarian | |
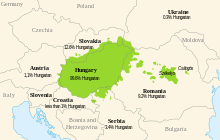 Regions of the Carpathian Basin where the Hungarian language is spoken | |
Hungarian is a Uralic language. The Hungarian name for the language is Magyar.
The Finno-Ugric languages also include Finnish, Estonian, Lappic (Sámi) and some other languages spoken in Russia: Khanty and Mansi are the most closely related to Hungarian. The Hungarian name for the language is Magyar.
Although Hungarian is not an Indo-European language, unlike most other European languages, its vocabulary has many words from Slavic and Turkic languages and also from German.
- ↑ Fenyvesi, Anna (2005), Hungarian Language Contact Outside Hungary, Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing, p. 11, ISBN 9027218587.