
Back Manhattan-projek Afrikaans مشروع مانهاتن Arabic Proyeutu Manhattan AST Manhetten layihəsi Azerbaijani Proyék Manhattan BAN Манхэтэнскі праект Byelorussian Проект „Манхатън“ Bulgarian ম্যানহাটন প্রকল্প Bengali/Bangla Raktres Manhattan Breton Projekt "Manhattan" BS
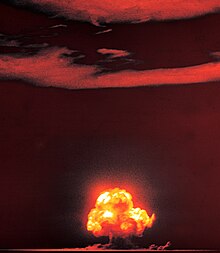
The Manhattan Project was the program based in the United States which tried to make the first nuclear weapons. The project went on during World War II, and was run by the U.S. Army. The head of the project was General Leslie R. Groves, who had led the building of the Pentagon. The top scientist on the project was Robert Oppenheimer, a famous physicist. The project cost $2 billion, and created many secret cities and bomb-making factories, such as a laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico, a nuclear reactor in Hanford, Washington, and a uranium processing plant in Oak Ridge, Tennessee.
The Manhattan Project had to find solutions to two difficulties. The first difficulty is how to make the special isotopes of uranium (uranium-235) or plutonium. This process is called separation and is very slow. The United States built very big buildings with three different kinds of machine for separation. They made enough fissionable special isotopes for a few nuclear weapons. The second difficulty was how to make a bomb that will produce a big nuclear explosion every time. A weapon with a bad design can make a much smaller nuclear explosion. This is called a "fizzle". In July 1945, the Manhattan Project solved the two difficulties and made the first nuclear explosion. This test of a nuclear weapon was called "Trinity" and was a success.
The Manhattan Project created two nuclear bombs which the United States used against Japan in 1945.