
Back Ming-dinastie Afrikaans Ming-Dynastie ALS የሚንግ ሥርወ መንግሥት Amharic Dinastía Ming AN मिंग वंश ANP سلالة مينغ الحاكمة Arabic عيلة مينج ARZ Dinastía Ming AST Min sülaləsi Azerbaijani مین سولالهسی AZB
Great Ming 大明 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1368–1644 | |||||||||||
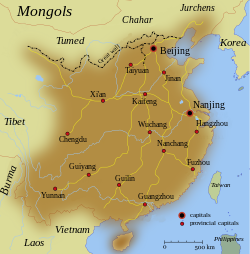 Ming China around 1580 | |||||||||||
| Capital | Nanjing (Yingtian prefecture) (1368–1644)[a] Beijing (Shuntian prefecture) (1403–1644)[b][c] | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Official language: Mandarin Other Chinese languages Other languages: Turki (Modern Uyghur), Old Uyghur language, Tibetan, Mongolian, Jurchen, others | ||||||||||
| Religion | Heaven worship, Taoism, Confucianism, Buddhism, Chinese folk religion, Islam, Roman Catholicism | ||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy | ||||||||||
| Emperor (皇帝) | |||||||||||
• 1368–1398 (first) | Hongwu Emperor | ||||||||||
• 1402-1424 | Yongle Emperor | ||||||||||
• 1627–1644 (last) | Chongzhen Emperor | ||||||||||
| Senior Grand Secretary | |||||||||||
• 1402–1407 | Xie Jin | ||||||||||
• 1644 | Wei Zaode | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established in Nanjing | 23 January 1368 | ||||||||||
• Beijing designated as capital | 28 October 1420 | ||||||||||
| 25 April 1644 | |||||||||||
• End of the Southern Ming | 1683 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 1415[1] | 6,500,000 km2 (2,500,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1393 | 65,000,000 | ||||||||||
• 1403 | 66,598,337¹ | ||||||||||
• 1500 | 125,000,000² | ||||||||||
• 1600 | 160,000,000³ | ||||||||||
| Currency | Paper money (1368–1450) Bimetallic: copper cashes (文, wén) in strings of coin and paper Silver taels (兩, liǎng) in sycees and by weight | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
Remnants of the Ming dynasty ruled southern China until 1662, and Taiwan until 1683 a dynastic period which is known as the Southern Ming. ¹The numbers are based on estimates made by CJ Peers in Late Imperial Chinese Armies: 1520–1840 ²According to A. G. Frank, ReOrient: global economy in the Asian Age, 1998, p. 109 ³According to A. Maddison, The World Economy Volume 1: A Millennial Perspective Volume 2, 2007, p. 238 | |||||||||||
Preview warning: Page using Template:Infobox country with unknown parameter "continent"
Preview warning: Page using Template:Infobox country with unknown parameter "region"
The Ming dynasty was the family of emperors who led China from AD 1368 to 1644. The name is also used to talk about the Ming Empire that they led and the 276 years in Chinese history that it lasted.
It is also famous for its pottery from Jingdezhen in Jiangxi and Dehua in Fujian.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
- ↑ Turchin, Peter; Adams, Jonathan M.; Hall, Thomas D (December 2006). "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires" (PDF). Journal of World-systems Research. 12 (2): 219–29. doi:10.5195/jwsr.2006.369. ISSN 1076-156X. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2010.