
Back صانعة Arabic Plastidlər Azerbaijani Пластыды Byelorussian Пластид Bulgarian প্লাস্টিড Bengali/Bangla Plastid BS Plastidi Catalan پلاستید CKB Plastid Czech Plastid Danish

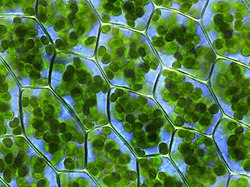
A plastid is a self-reproducing organelle of plants and algae. A plastome is the DNA genome of a plastid.[1]p341 They are like tiny machines inside cells: each makes or stores important chemicals used by the plant.
Examples of plastids are:
- Chloroplasts: photosynthesis; other plastids may have developed from chloroplasts. Etioplasts are chloroplasts which have not been exposed to light.
- Chromoplasts: pigment synthesis and storage.
- Leucoplasts: colourless, make terpenes such as resin. Sometimes they develop into more specialized types of plastid:
- ↑ King R.C. Stansfield W.D. & Mulligan P.K. 2006. A dictionary of genetics, 7th ed. Oxford.