
Back Xenondifluoried Afrikaans ثنائي فلوريد الزينون Arabic زنون دیفلورید AZB Difluorur de xenó Catalan Fluorid xenonatý Czech Xenondifluorid German Διφθοριούχο ξένο Greek Difluoruro de xenón Spanish زنون دیفلورید Persian Ksenondifluoridi Finnish

| |
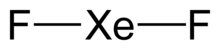
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Xenon difluoride
Xenon(II) fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.850 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| F2Xe | |
| Molar mass | 169.290 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 4.32 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 128.6 °C (263.5 °F; 401.8 K)[2] |
| 25 g/L (0 °C) | |
| Vapor pressure | 6.0×102 Pa[1] |
| Structure | |
| parallel linear XeF2 units | |
| Linear | |
| 0 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
254 J·mol−1·K−1[3] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−108 kJ·mol−1[3] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive to exposed tissues. Releases toxic compounds on contact with moisture.[5] |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H272, H301, H314, H330 | |
| P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+P310+P330, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338, P331, P363, P370+P378, P403+P233, P405, P501[4] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | PELCHEM MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Xenon dichloride Xenon dibromide |
Other cations
|
Krypton difluoride Radon difluoride |
Related compounds
|
Xenon tetrafluoride Xenon hexafluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.
It has a nauseating odour and low vapor pressure.[6]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
tramsekwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Hindermann, D. K., Falconer, W. E. (1969). "Magnetic Shielding of 19F in XeF2". J. Chem. Phys. 50 (3): 1203. Bibcode:1969JChPh..50.1203H. doi:10.1063/1.1671178.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ "Sigma Aldrich Xenon Difluoride SDS". Sigma Aldrich. Millpore Sigma. Retrieved 2 November 2022.
- ^ "MSDS: xenon difluoride" (PDF). BOC Gases. Retrieved 2010-06-01.
- ^ James L. Weeks; Max S. Matheson (1966). "Xenon Difluoride". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 8. pp. 260–264. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch69. ISBN 9780470132395.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help)
